ChIP, ChIP-seq
Product Information
Storage
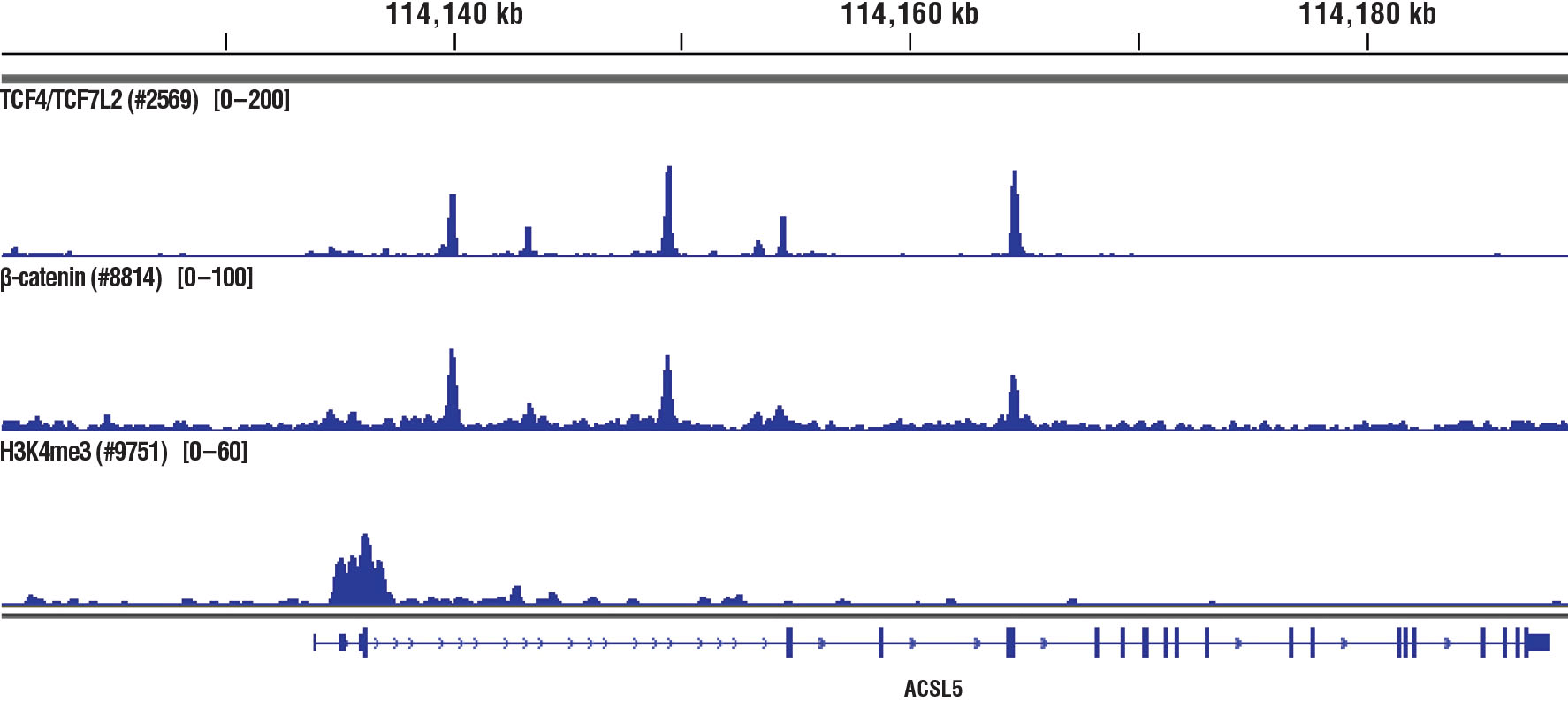
Specificity / Sensitivity
Product Description
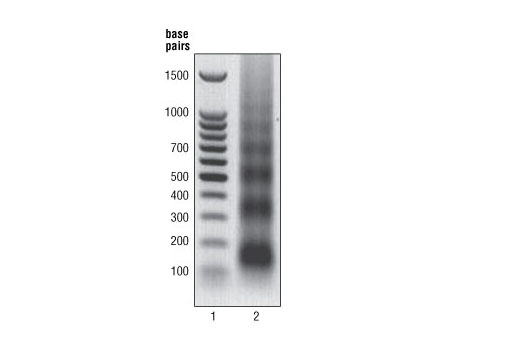
Cells are fixed with formaldehyde and lysed, and chromatin is fragmented by partial digestion with Micrococcal Nuclease to obtain chromatin fragments of 1 to 5 nucleosomes. Enzymatic fragmentation of chromatin is much milder than sonication and eliminates problems resulting from variability in sonication power and emulsification of chromatin during sonication, which can result in incomplete fragmentation of chromatin or loss of antibody epitopes due to protein denaturation and degradation. Chromatin immunoprecipitations are performed using ChIP-validated antibodies and ChIP-Grade Protein G Magnetic Beads. After reversal of protein-DNA cross-links, the DNA is purified using DNA purification spin columns, allowing for easy and efficient recovery of DNA and removal of protein contaminants without the need for phenol/chloroform extractions and ethanol precipitations. The enrichment of particular DNA sequences during immunoprecipitation can be analyzed by a variety of methods, including standard PCR, quantitative real-time PCR, or amplification for ChIP on chip, sequencing or cloning techniques. This kit is compatible with ChIP-seq.
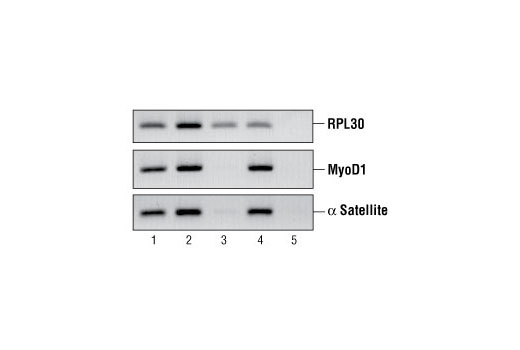
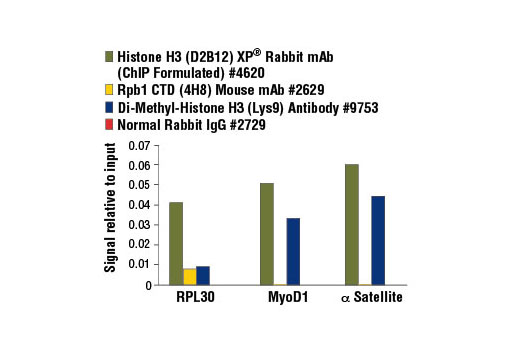
All of our SimpleChIP® ChIP kits also provide important controls to ensure a successful ChIP experiment. The kit contains a positive control Histone H3 Antibody, a negative control Normal Rabbit IgG Antibody and primer sets for PCR detection of the human and mouse ribosomal protein L30 (RPL30) genes. Histone H3 is a core component of chromatin and is bound to most DNA sequences throughout the genome, including the RPL30 locus. Thus, the Histone H3 Antibody provides a universal positive control that should enrich for almost any locus examined.
Background
The chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay is a powerful and versatile technique used for probing protein-DNA interactions within the natural chromatin context of the cell (1,2). This assay can be used to identify multiple proteins associated with a specific region of the genome, or the opposite, to identify the many regions of the genome bound by a particular protein (3-6). It can be used to determine the specific order of recruitment of various proteins to a gene promoter or to "measure" the relative amount of a particular histone modification across an entire gene locus (3,4). In addition to histone proteins, the ChIP assay can be used to analyze binding of transcription factors and co-factors, DNA replication factors and DNA repair proteins. When performing the ChIP assay, cells or tissues are first fixed with formaldehyde, a reversible protein-DNA cross-linking agent that "preserves" the protein-DNA interactions occurring in the cell (1,2). Cells are lysed and chromatin is harvested and fragmented using either sonication or enzymatic digestion. The chromatin is then immunoprecipitated with antibodies specific to a particular protein or histone modification. Any DNA sequences that are associated with the protein or histone modification of interest will co-precipitate as part of the cross-linked chromatin complex and the relative amount of that DNA sequence will be enriched by the immunoselection process. After immunoprecipitation, the protein-DNA cross-links are reversed and the DNA is purified. Standard PCR or Quantitative Real-Time PCR can be used to measure the amount of enrichment of a particular DNA sequence by a protein-specific immunoprecipitation (1,2). Alternatively, the ChIP assay can be combined with genomic tiling micro-array (ChIP on chip) techniques, high throughput sequencing, or cloning strategies, all of which allow for genome-wide analysis of protein-DNA interactions and histone modifications (5-8).
- Orlando, V. (2000) Trends Biochem Sci 25, 99-104.
- Liu, Q. et al. (2000) Genes Dev 14, 1448-59.
- Kuo, M.H. and Allis, C.D. (1999) Methods 19, 425-33.
- Zhao, H. and Piwnica-Worms, H. (2001) Mol Cell Biol 21, 4129-39.
- Agalioti, T. et al. (2000) Cell 103, 667-78.
- Jiang, K. et al. (2003) J Biol Chem 278, 25207-17.
- Soutoglou, E. and Talianidis, I. (2002) Science 295, 1901-4.
- Martin, S.A. and Ouchi, T. (2008) Mol Cancer Ther 7, 2509-16.
- Mikkelsen, T.S. et al. (2007) Nature 448, 553-60.
- Chen, M.S. et al. (2003) Mol Cell Biol 23, 7488-97.
- Lee, T.I. et al. (2006) Cell 125, 301-13.
- Zeng, Y. et al. (1998) Nature 395, 507-10.
- Weinmann, A.S. and Farnham, P.J. (2002) Methods 26, 37-47.
- Löffler, H. et al. (2006) Cell Cycle 5, 2543-7.
- Wells, J. and Farnham, P.J. (2002) Methods 26, 48-56.
- Zachos, G. et al. (2007) Dev Cell 12, 247-60.
- Garber, K. (2005) J Natl Cancer Inst 97, 1026-8.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Applications Key
ChIP: Chromatin IP ChIP-seq: Chromatin IP-seq
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
使用に関する制限
法的な権限を与えられたCSTの担当者が署名した書面によって別途明示的に合意された場合を除き、 CST、その関連会社または代理店が提供する製品には以下の条件が適用されます。お客様が定める条件でここに定められた条件に含まれるものを超えるもの、 または、ここに定められた条件と異なるものは、法的な権限を与えられたCSTの担当者が別途書面にて受諾した場合を除き、拒絶され、 いかなる効力も効果も有しません。
研究専用 (For Research Use Only) またはこれに類似する表示がされた製品は、 いかなる目的についても FDA または外国もしくは国内のその他の規制機関により承認、認可または許可を受けていません。 お客様は製品を診断もしくは治療目的で使用してはならず、また、製品に表示された内容に違反する方法で使用してはなりません。 CST が販売または使用許諾する製品は、エンドユーザーであるお客様に対し、使途を研究および開発のみに限定して提供されるものです。 診断、予防もしくは治療目的で製品を使用することまたは製品を再販売 (単独であるか他の製品等の一部であるかを問いません) もしくはその他の商業的利用の目的で購入することについては、CST から別途許諾を得る必要があります。 お客様は以下の事項を遵守しなければなりません。(a) CST の製品 (単独であるか他の資材と一緒であるかを問いません) を販売、使用許諾、貸与、寄付もしくはその他の態様で第三者に譲渡したり使用させたりしてはなりません。また、商用の製品を製造するために CST の製品を使用してはなりません。(b) 複製、改変、リバースエンジニアリング、逆コンパイル、 分解または他の方法により製品の構造または技術を解明しようとしてはなりません。また、 CST の製品またはサービスと競合する製品またはサービスを開発する目的で CST の製品を使用してはなりません。(c) CST の製品の商標、商号、ロゴ、特許または著作権に関する通知または表示を除去したり改変したりしてはなりません。(d) CST の製品をCST 製品販売条件(CST’s Product Terms of Sale) および該当する書面のみに従って使用しなければなりません。(e) CST の製品に関連してお客様が使用する第三者の製品またはサービスに関する使用許諾条件、 サービス提供条件またはこれに類する合意事項を遵守しなければなりません。