| Kit Includes* | Quantity | Applications | Dilution | Isotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
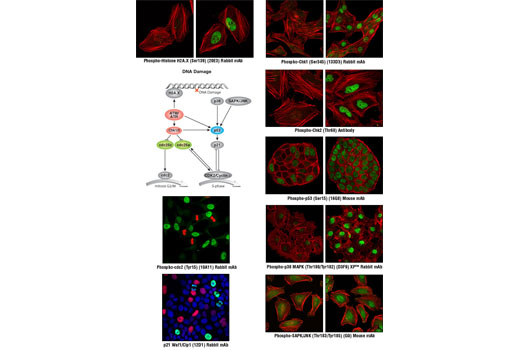
| Phospho-Histone H2A.X (Ser139) (20E3) Rabbit mAb | 140 µl | HCA, ICW, IF-IC | 1:10 | Rabbit IgG |
| Phospho-Chk1 (Ser345) (133D3) Rabbit mAb | 140 µl | HCA, ICW, IF-IC | 1:10 | Rabbit IgG |
| Phospho-Chk2 (Thr68) Antibody | 140 µl | HCA, ICW, IF-IC | 1:10 | Rabbit IgG |
| Phospho-p53 (Ser15) (16G8) Mouse mAb | 140 µl | HCA, ICW, IF-IC | 1:10 | Mouse IgG1 |
| p21 Waf1/Cip1 (12D1) Rabbit mAb | 140 µl | HCA, ICW, IF-IC | 1:10 | Rabbit IgG |
| Phospho-cdc2 (Tyr15) (10A11) Rabbit mAb | 140 µl | HCA, ICW, IF-IC | 1:10 | Rabbit IgG |
| Phospho-p38 MAPK (Thr180/Tyr182) (D3F9) XP™ Rabbit mAb | 140 µl | HCA, ICW, IF-IC | 1:10 | Rabbit IgG |
| Phospho-SAPK/JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) (G9) Mouse mAb | 140 µl | HCA, ICW, IF-IC | 1:10 | Mouse IgG1 |
*Component formulation specific to kit.
Applications Key: HCA=High Content Analysis, ICW=In-Cell Western, IF-IC=Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry)
Description
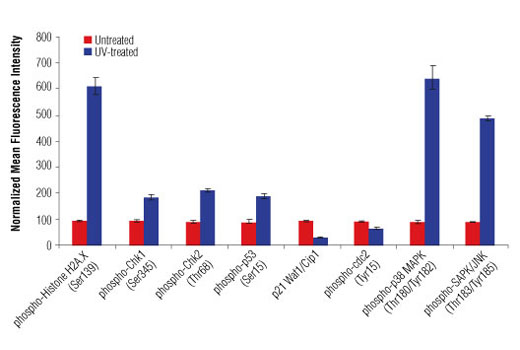
CST’s PathScan® Multi-Target HCA DNA Damage Kit contains eight primary antibodies that target the DNA damage cellular signaling pathway. This kit is designed to elucidate the signaling occurring through key pathway nodes using automated imaging or laser scanning platforms or manual immunofluorescent microscopy. The kit provides the investigator with a quick and easy means to choose the endpoints that will be the most robust and useful for subsequent studies, whether large high content/high throughput screening projects or single small-scale experiments. The antibodies are supplied at 10X of their optimal dilution for immunofluorescent applications. This allows the antibodies to be easily diluted to their 1X working concentrations and dispensed into multi-well plates or slides. 140 μl of each antibody is supplied, which is sufficient for 24 wells on 96-well plates (50 μl 1X per well) or one row on two 96-well plates.
Storage
Background
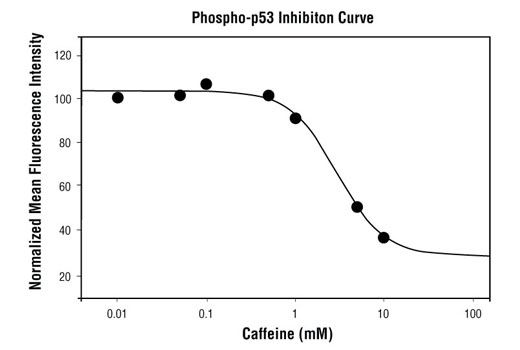
Cell cycle control involves an ordered series of cellular signaling events designed to maintain the integrity and proper function of cells and biological pathways. Cells have evolved complex mechanisms, collectively termed the DNA damage checkpoint, to modulate cell cycle progression in response to genomic insult. Damage to DNA caused by either internal or external sources such as UV light, ionizing radiation, genotoxic agents, etc. initiates a cascade of events that blocks cell cycle progression to either allow time to repair damaged DNA, or activate cell death pathways if too much damage has been incurred. Monitoring the signaling components of the DNA damage pathway is important to aid in understanding the aberrant cellular signaling associated with unchecked cell cycle control in disease states such as cancer. Cell cycle progression can be affected by the DNA damage checkpoint at the G1/S transition, during S phase, or at the G2/M phase transition. At G2/M, cdc2/cyclin B activity acts as a master regulator of entry into mitosis (1). The cdc25C phosphatase removes inhibitory phosphorylation on Thr14 and Tyr15 of cdc2, allowing for maximal activation of cdc2/cyclin B (1,2). When DNA damage occurs, a signaling cascade is activated that inhibits the ability of cdc25 to activate cdc2/cyclin B. A proximal event in the signaling pathway is localization of Ser139-phosphorylated histone H2A.X to sites of DNA damage at subnuclear foci (3). Histone H2A.X and other mediators recruit additional signaling molecules to the site of the damage, activating the ATM/ATR kinases, the central mediators of the DNA damage response. ATM is primarily activated by double strand breaks of DNA (4,5), while ATR is activated by a variety of DNA lesions and replication stresses (6). ATM/ATR in turn initiate two parallel cascades that inactivate the cdc2/cyclin B complex (7). The first cascade rapidly inhibits progression into mitosis through the activation of the Chk kinases (Chk1 for ATR and Chk2 for ATM), which phosphorylate and inactivate cdc25, preventing activation of cdc2/cyclin B (8-10). The more long-term second cascade involves phosphorylation of the tumor suppressor protein p53, leading to either cell cycle arrest and DNA repair or apoptosis through regulation of p53 downstream effectors, including the tumor suppressor protein p21 Waf1/Cip1 (11). Upon DNA damage, p53 is phosphorylated at a number of sites and up-regulates p21 transcription via a p53 responsive element. p21 expression can block cell cycle progression by inhibiting a subset of the cyclin-dependent kinases including cdc2 (12,13). In addition to canonical ATM/ATR checkpoint signaling, the SAPK/JNK and p38 MAP kinase pathways are activated by a variety of cellular stresses including inflammatory cytokines, UV light, and growth factors (14,15). These stress-activated pathways contribute to G2/M checkpoint control through activation of p53 and other MAPK substrates, such as MAPKAPK-2, which can directly affect components of the checkpoint cascade, such as cdc25 (8).
- Stark, G.R. and Taylor, W.R. (2006) Mol Biotechnol 32, 227-48.
- Hoffmann, I. et al. (1993) EMBO J 12, 53-63.
- Rogakou, E.P. et al. (1999) J Cell Biol 146, 905-16.
- Cliby, W.A. et al. (1998) EMBO J 17, 159-69.
- Tibbetts, R.S. et al. (1999) Genes Dev 13, 152-7.
- Kastan, M.B. and Lim, D.S. (2000) Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1, 179-86.
- Kobayashi, J. et al. (2009) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 380, 752-7.
- Reinhardt, H.C. and Yaffe, M.B. (2009) Curr Opin Cell Biol 21, 245-55.
- Blasina, A. et al. (1999) Curr Biol 9, 1-10.
- Furnari, B. et al. (1999) Mol Biol Cell 10, 833-45.
- Levine, A.J. (1997) Cell 88, 323-31.
- Wang, Y. and Prives, C. (1995) Nature 376, 88-91.
- Stuart, S.A. and Wang, J.Y. (2009) J Biol Chem 284, 15061-70.
- Pearce, A.K. and Humphrey, T.C. (2001) Trends Cell Biol 11, 426-33.
- Johnson, G.L. and Lapadat, R. (2002) Science 298, 1911-2.
Background References
Trademarks and Patents
使用に関する制限
法的な権限を与えられたCSTの担当者が署名した書面によって別途明示的に合意された場合を除き、 CST、その関連会社または代理店が提供する製品には以下の条件が適用されます。お客様が定める条件でここに定められた条件に含まれるものを超えるもの、 または、ここに定められた条件と異なるものは、法的な権限を与えられたCSTの担当者が別途書面にて受諾した場合を除き、拒絶され、 いかなる効力も効果も有しません。
研究専用 (For Research Use Only) またはこれに類似する表示がされた製品は、 いかなる目的についても FDA または外国もしくは国内のその他の規制機関により承認、認可または許可を受けていません。 お客様は製品を診断もしくは治療目的で使用してはならず、また、製品に表示された内容に違反する方法で使用してはなりません。 CST が販売または使用許諾する製品は、エンドユーザーであるお客様に対し、使途を研究および開発のみに限定して提供されるものです。 診断、予防もしくは治療目的で製品を使用することまたは製品を再販売 (単独であるか他の製品等の一部であるかを問いません) もしくはその他の商業的利用の目的で購入することについては、CST から別途許諾を得る必要があります。 お客様は以下の事項を遵守しなければなりません。(a) CST の製品 (単独であるか他の資材と一緒であるかを問いません) を販売、使用許諾、貸与、寄付もしくはその他の態様で第三者に譲渡したり使用させたりしてはなりません。また、商用の製品を製造するために CST の製品を使用してはなりません。(b) 複製、改変、リバースエンジニアリング、逆コンパイル、 分解または他の方法により製品の構造または技術を解明しようとしてはなりません。また、 CST の製品またはサービスと競合する製品またはサービスを開発する目的で CST の製品を使用してはなりません。(c) CST の製品の商標、商号、ロゴ、特許または著作権に関する通知または表示を除去したり改変したりしてはなりません。(d) CST の製品をCST 製品販売条件(CST’s Product Terms of Sale) および該当する書面のみに従って使用しなければなりません。(e) CST の製品に関連してお客様が使用する第三者の製品またはサービスに関する使用許諾条件、 サービス提供条件またはこれに類する合意事項を遵守しなければなりません。