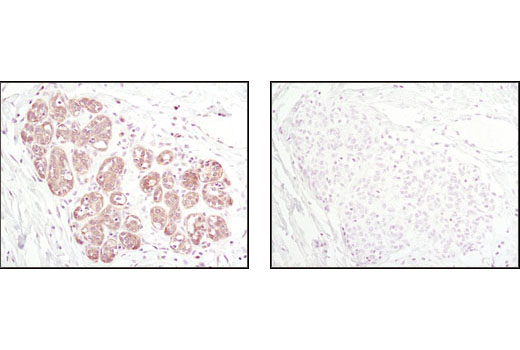
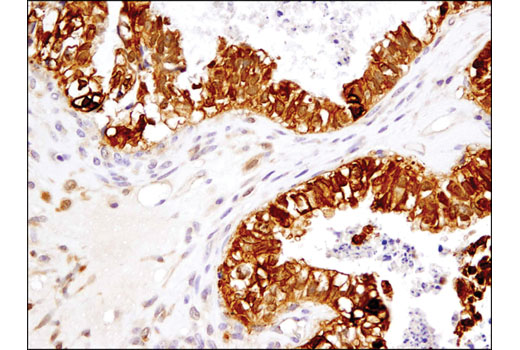
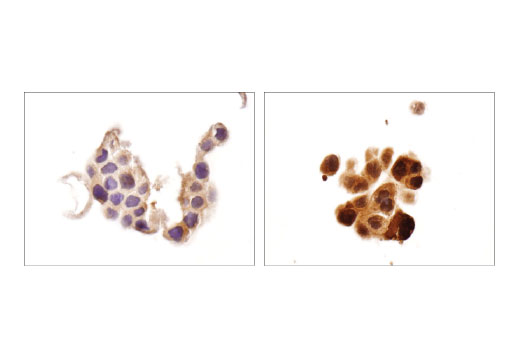
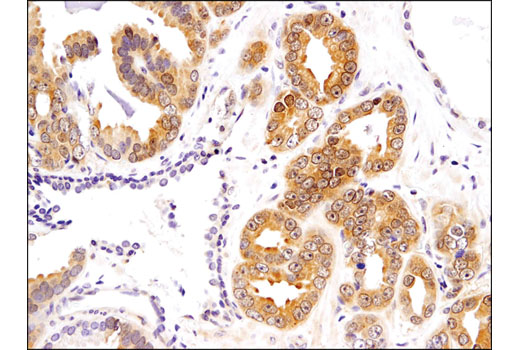
| Product Includes | Product # | Quantity | Mol. Wt | Isotype/Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
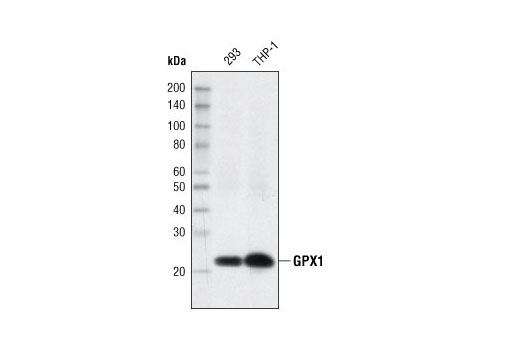
| GPX1 (C8C4) Rabbit mAb | 3286 | 20 µl | 22 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
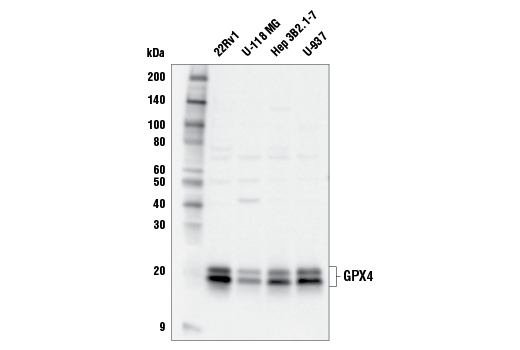
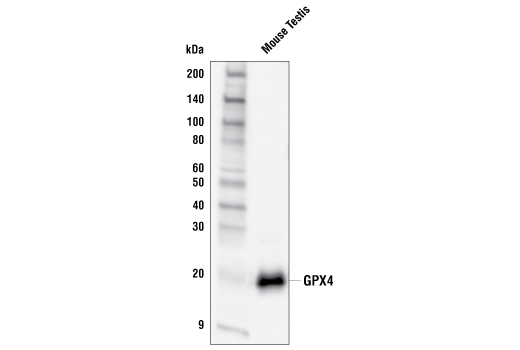
| GPX4 Antibody | 52455 | 20 µl | 20, 22 kDa | Rabbit |
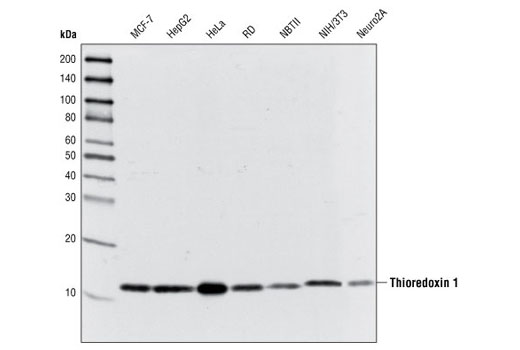
| Thioredoxin 1 (C63C6) Rabbit mAb | 2429 | 20 µl | 12 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
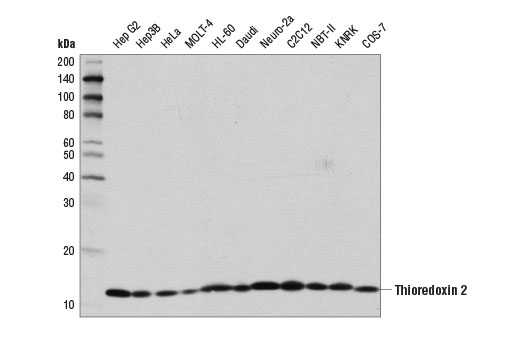
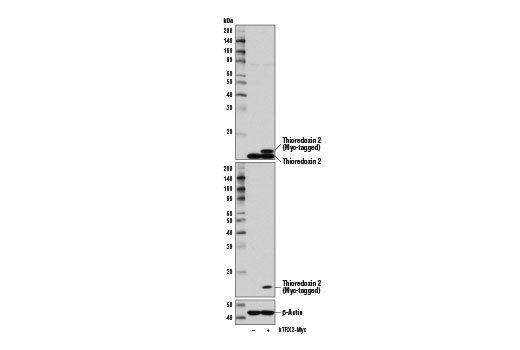
| Thioredoxin 2 (D1C9L) Rabbit mAb | 14907 | 20 µl | 13 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
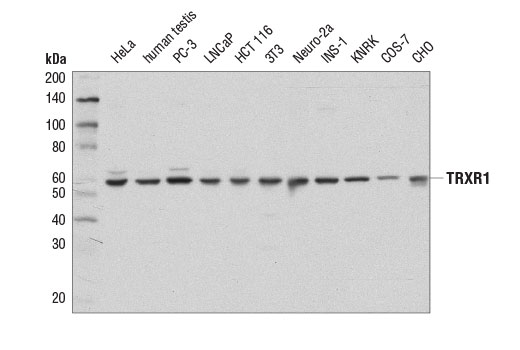
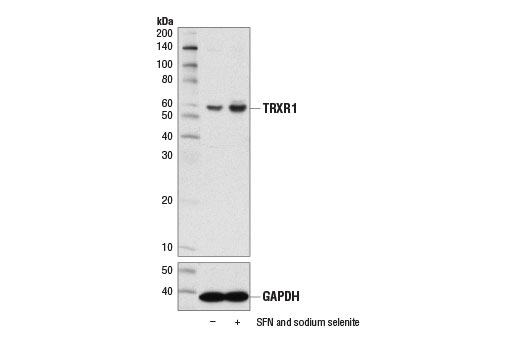
| TRXR1 (D1T3D) Rabbit mAb | 15140 | 20 µl | 55 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
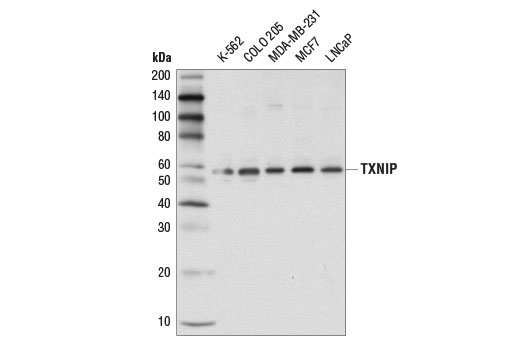
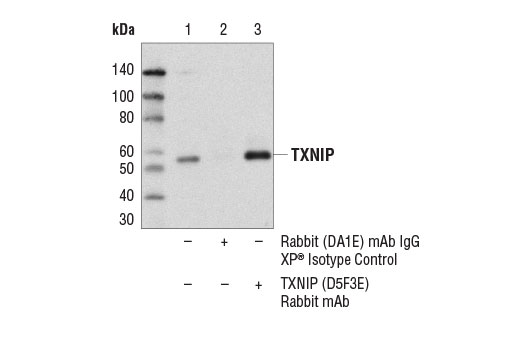
| TXNIP (D5F3E) Rabbit mAb | 14715 | 20 µl | 55 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
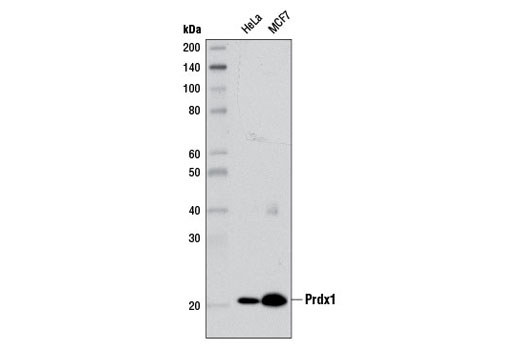
| Prdx1 (D5G12) Rabbit mAb | 8499 | 20 µl | 21 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
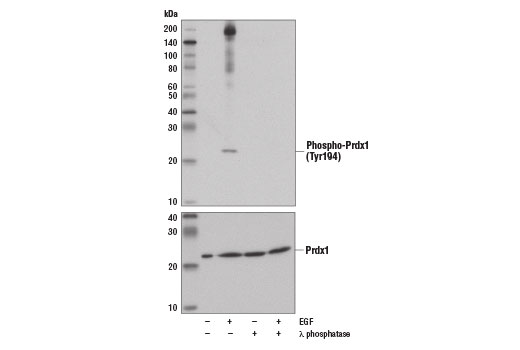
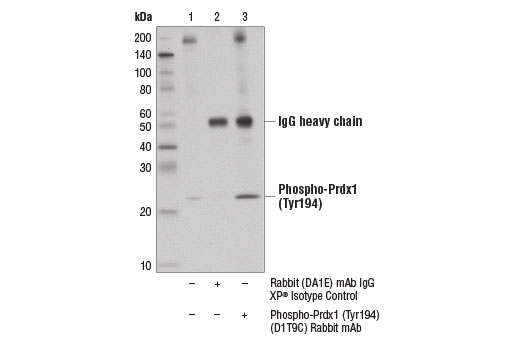
| Phospho-Prdx1 (Tyr194) (D1T9C) Rabbit mAb | 14041 | 20 µl | 21 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
| Anti-rabbit IgG, HRP-linked Antibody | 7074 | 100 µl | Goat |
Please visit cellsignal.com for individual component applications, species cross-reactivity, dilutions, protocols, and additional product information.
Description
The Redox Homeostasis and Signaling Antibody Sampler Kit provides an economical means of detecting select components involved in redox homeostasis and signaling. The kit contains enough primary antibodies to perform at least two western blot experiments per antibody.
Storage
Background
Glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPX1) is a cytosolic selenoprotein which reduces hydrogen peroxide to water (1). GPX1 is the most abundant and ubiquitous among the five GPX isoforms identified so far (2). It is an important component in the anti-oxidative defense in cells and is associated with a variety of disease conditions, such as colon cancer (3), coronary artery disease (4), and insulin resistance (1). The selenoprotein glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) is a master regulator of ferroptosis, a form of programmed cell death induced by the iron-dependent lipid peroxidation (5,6). GPX4 converts lipid hydroperoxides to non-toxic lipid alcohols, therefore preventing ferroptosis (6). Research studies show that selenium enhances GPX4 expression and inhibits ferroptotic death to protect neurons (7). In addition, some therapy-resistant cancer cells depend on GPX4 to survive. Loss of GPX4 leads to ferroptosis and thus prevents tumor relapse in mice (8). Furthermore, redox homeostasis mediated by GPX4 is essential for the activation of the cytosolic DNA-sensing cGAS-STING pathway and initiation of the subsequent innate immune response (9). Thioredoxin is a small redox protein found in many eukaryotes and prokaryotes. A pair of cysteines within a highly conserved, active site sequence can be oxidized to form a disulfide bond that is then reduced by thioredoxin reductase (10). Multiple forms of thioredoxin have been identified, including cytosolic thioredoxin 1 (TRX1) and mitochondrial thioredoxin 2 (TRX2). Thioredoxin participates in many cellular processes, including redox signaling, response to oxidative stress, and protein reduction (10). A potential role of thioredoxin in human disorders such as cancer, aging, and heart disease is currently under investigation (11). Thioredoxin can play a key role in cancer progression because it acts as a negative regulator of the proapoptotic kinase ASK1 (12). Changes in thioredoxin expression have been associated with meningococcal septic shock and acute lung injury (13,14). TRXR1 (thioredoxin reductase 1) is a selenocysteine-containing protein that is involved in redox homeostasis (15-20). Its canonical target is thioredoxin, another redox protein (15). Together, they are involved in many functions such as antioxidant regulation (17-20), cell proliferation (16,17,19), DNA replication (16,17), and transcription (17,19). TRXR1 is also capable of reducing a wide array of cellular proteins (15,17). Selenium deficiency, either by diet modification (16,20) or introduction of methylmercury (18), hinders proper expression and function of TRXR1. It is possible that this effect, which results in a higher oxidative state, is a result of the selenocysteine codon (UGA) being read as a STOP codon in the absence of adequate selenium (18). The functions of TRXR1 in cell proliferation and antioxidant defense make it a potential therapeutic target. The ubiquitously expressed thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) binds and inhibits thioredoxin to regulate cellular redox state (21-23). Research studies demonstrate that hyperglycemia induces TXNIP expression and increases cellular oxidative stress (21). In addition, these studies show that TXNIP reduces glucose uptake directly by binding the glucose transporter Glut1 to stimulate receptor internalization or indirectly by reducing Glut1 mRNA levels (23). Additional studies indicate that TXNIP plays a role in the regulation of insulin mRNA transcription (24). Microarray analyses indicate that TXNIP acts downstream of PPARγ and is a putative tumor suppressor that may control thyroid cancer cell progression (25). In addition, the TXNIP protein may be a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and some disorders related to ER-stress (26). Prdx1 belongs to a family of non-seleno peroxidases that function as H2O2 scavengers. The transient phosphorylation of Prdx1 at Tyr194 leads to inactivation of Prdx1 (27).
- McClung, J.P. et al. (2004) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101, 8852-7.
- Hamanishi, T. et al. (2004) Diabetes 53, 2455-60.
- Drew, J.E. et al. (2005) FEBS Lett 579, 6135-9.
- Winter, J.P. et al. (2003) Coron Artery Dis 14, 149-53.
- Wenzel, S.E. et al. (2017) Cell 171, 628-641.e26.
- Bersuker, K. et al. (2019) Nature 575, 688-92.
- Alim, I. et al. (2019) Cell 177, 1262-1279.e25.
- Hangauer, M.J. et al. (2017) Nature 551, 247-50.
- Jia, M. et al. (2020) Nat Immunol 21, 727-35.
- Watson, W.H. et al. (2004) Toxicol Sci 78, 3-14.
- Burke-Gaffney, A. et al. (2005) Trends Pharmacol Sci 26, 398-404.
- Saitoh, M. et al. (1998) EMBO J 17, 2596-606.
- Callister, M.E. et al. (2007) Intensive Care Med 33, 364-7.
- Callister, M.E. et al. (2006) Thorax 61, 521-7.
- Turanov, A.A. et al. (2010) Biochem J 430, 285-93.
- Gasdaska, P.Y. et al. (1995) FEBS Lett 373, 5-9.
- Gromer, S. et al. (2004) Med Res Rev 24, 40-89.
- Usuki, F. et al. (2011) J Biol Chem 286, 6641-9.
- Pappas, A.C. et al. (2008) Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 151, 361-72.
- Müller, M. et al. (2010) Genes Nutr 5, 297-307.
- Schulze, P.C. et al. (2004) J Biol Chem 279, 30369-74.
- Saxena, G. et al. (2010) J Biol Chem 285, 3997-4005.
- Wu, N. et al. (2013) Mol Cell 49, 1167-75.
- Xu, G. et al. (2013) Nat Med 19, 1141-6.
- Morrison, J.A. et al. (2014) Mol Cancer 13, 62.
- Robinson, K.A. et al. (2013) J Mol Endocrinol 50, 59-71.
- Woo, H.A. et al. (2010) Cell 140, 517-28.
Background References
Trademarks and Patents
使用に関する制限
法的な権限を与えられたCSTの担当者が署名した書面によって別途明示的に合意された場合を除き、 CST、その関連会社または代理店が提供する製品には以下の条件が適用されます。お客様が定める条件でここに定められた条件に含まれるものを超えるもの、 または、ここに定められた条件と異なるものは、法的な権限を与えられたCSTの担当者が別途書面にて受諾した場合を除き、拒絶され、 いかなる効力も効果も有しません。
研究専用 (For Research Use Only) またはこれに類似する表示がされた製品は、 いかなる目的についても FDA または外国もしくは国内のその他の規制機関により承認、認可または許可を受けていません。 お客様は製品を診断もしくは治療目的で使用してはならず、また、製品に表示された内容に違反する方法で使用してはなりません。 CST が販売または使用許諾する製品は、エンドユーザーであるお客様に対し、使途を研究および開発のみに限定して提供されるものです。 診断、予防もしくは治療目的で製品を使用することまたは製品を再販売 (単独であるか他の製品等の一部であるかを問いません) もしくはその他の商業的利用の目的で購入することについては、CST から別途許諾を得る必要があります。 お客様は以下の事項を遵守しなければなりません。(a) CST の製品 (単独であるか他の資材と一緒であるかを問いません) を販売、使用許諾、貸与、寄付もしくはその他の態様で第三者に譲渡したり使用させたりしてはなりません。また、商用の製品を製造するために CST の製品を使用してはなりません。(b) 複製、改変、リバースエンジニアリング、逆コンパイル、 分解または他の方法により製品の構造または技術を解明しようとしてはなりません。また、 CST の製品またはサービスと競合する製品またはサービスを開発する目的で CST の製品を使用してはなりません。(c) CST の製品の商標、商号、ロゴ、特許または著作権に関する通知または表示を除去したり改変したりしてはなりません。(d) CST の製品をCST 製品販売条件(CST’s Product Terms of Sale) および該当する書面のみに従って使用しなければなりません。(e) CST の製品に関連してお客様が使用する第三者の製品またはサービスに関する使用許諾条件、 サービス提供条件またはこれに類する合意事項を遵守しなければなりません。