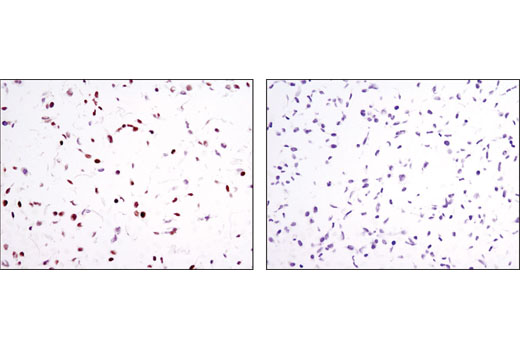
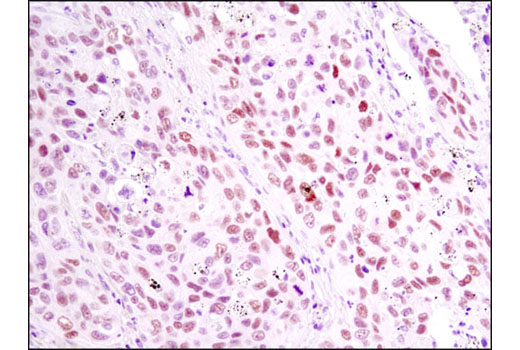
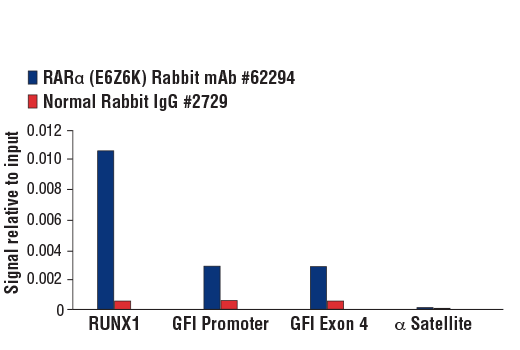
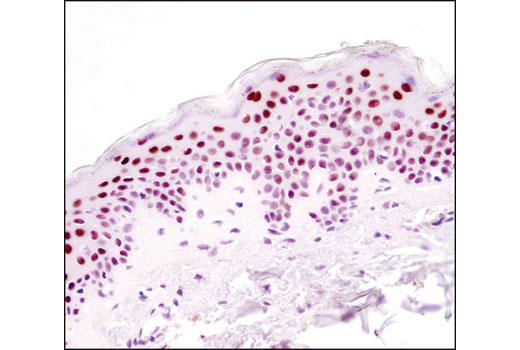
| Product Includes | Product # | Quantity | Mol. Wt | Isotype/Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
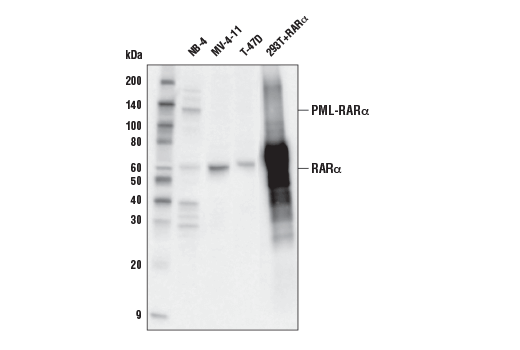
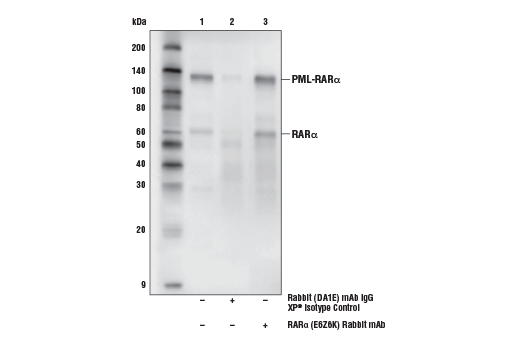
| RARα (E6Z6K) Rabbit mAb | 62294 | 20 µl | 60 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
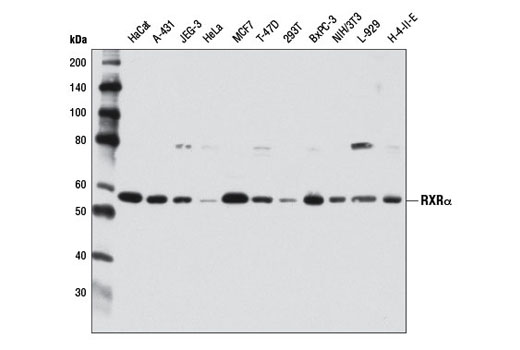
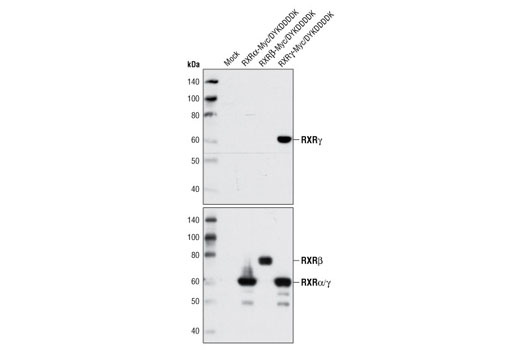
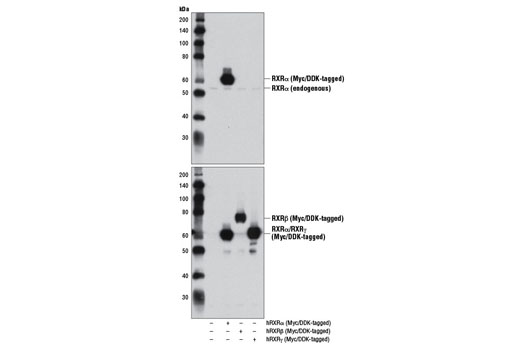
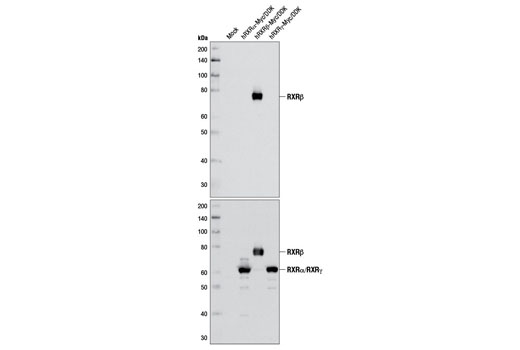
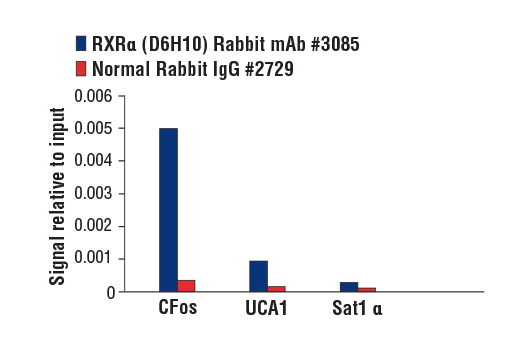
| RXRα (D6H10) Rabbit mAb | 3085 | 20 µl | 53 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
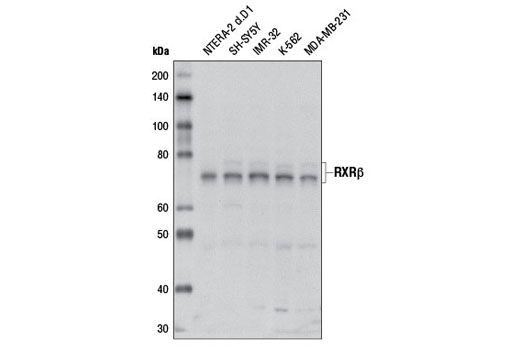
| RXRβ Antibody | 8715 | 20 µl | 70-72 kDa | Rabbit |
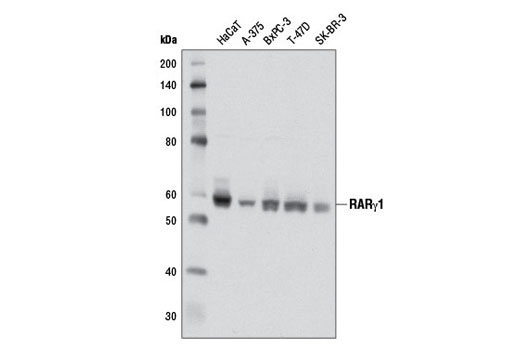
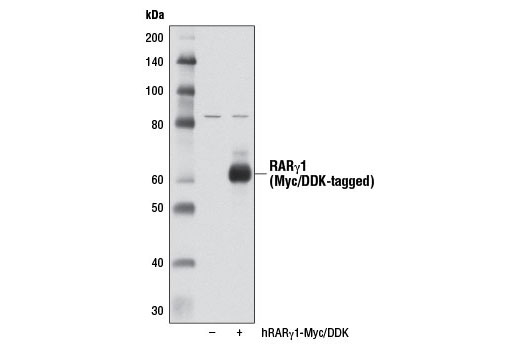
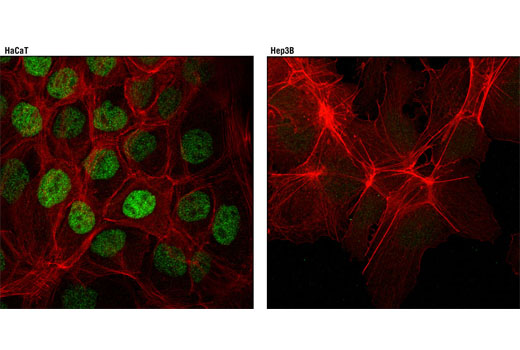
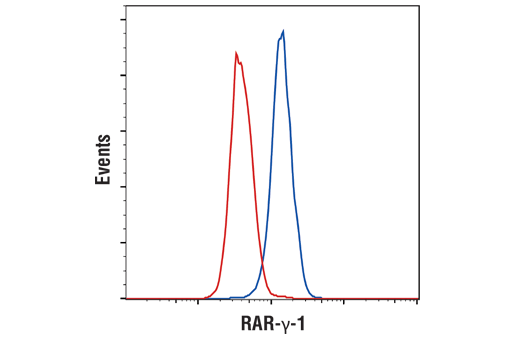
| RARγ1 (D3A4) XP® Rabbit mAb | 8965 | 20 µl | 58 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
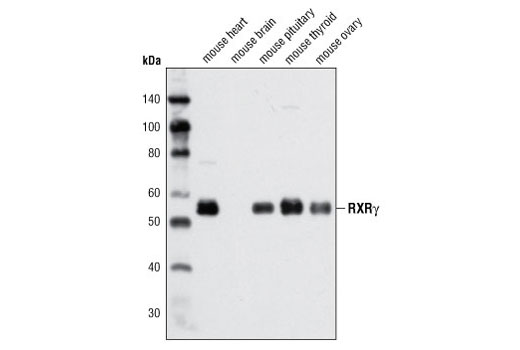
| RXRγ Antibody | 5629 | 20 µl | 55 kDa | Rabbit |
| Anti-rabbit IgG, HRP-linked Antibody | 7074 | 100 µl | Goat |
Please visit cellsignal.com for individual component applications, species cross-reactivity, dilutions, protocols, and additional product information.
Description
The Retinoic Acid and Retinoid X Receptors Antibody Sampler Kit provides an economical means to investigate the expression of various subtypes of retinoic acid and retinoid X receptors. The kit contains enough primary antibody to perform two western blot experiments per primary.
Storage
Background
Nuclear retinoic acid (RA) receptors (RARs) consist of three subtypes encoded by separate genes: α (NR1B1), β (NR1B2), and γ (NR1B3). For each subtype, there are at least two isoforms, which are generated by differential promoter usage and alternative splicing and differ only in their N-terminal regions. Retinoids, which are metabolites of vitamin A, serve as ligands for RARs (1). RARs function as ligand-dependent transcriptional regulators and are found to be heterodimerized with retinoid X receptors (RXRs). These transcriptionally active dimers regulate the expression of genes involved in cellular differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis (2,3). Consequently, RARs play critical roles in a variety of biological processes, including development, reproduction, immunity, and organogenesis (4-6). RAR mutations, fusion proteins, altered expression levels, or aberrant post-translational modifications result in multiple diseases due to altered RAR function and disruption of homeostasis.
In contrast to the ubiquitously expressed RARα subtype, RARγ displays a complex tissue-specific expression pattern (7). The hematopoietic system expresses significant levels of RARγ, and a recent study identified a role for RARγ in hematopoietic stem cell maintenance (8). RARγ is the predominant subtype in human and mouse epidermis, representing 90% of the RARs in this tissue (9-11). Given the high level of RARγ expression in the skin, it has been suggested that this nuclear receptor participates in a transcriptional program that governs maintenance and differentiation of normal epidermis and skin appendages. The transcriptional activity of RARγ is under stringent control, in part, through retinoic acid-induced phosphorylation and proteasomal degradation (12).
The human retinoid X receptors (RXRs) are encoded by three distinct genes (RXRα, RXRβ, and RXRγ) and bind selectively and with high affinity to the vitamin A derivative, 9-cis-retinoic acid. RXRs are type-II nuclear hormone receptors that are largely localized to the nuclear compartment independent of ligand binding. Nuclear RXRs form heterodimers with nuclear hormone receptor subfamily 1 proteins, including thyroid hormone receptor, retinoic acid receptors, vitamin D receptor, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors, liver X receptors, and farnesoid X receptor (13). Since RXRs heterodimerize with multiple nuclear hormone receptors, they play a central role in transcriptional control of numerous hormonal signaling pathways by binding to cis-acting response elements in the promoter/enhancer region of target genes (14).
- Rochette-Egly, C. and Germain, P. (2009) Nucl Recept Signal 7, e005.
- Delacroix, L. et al. (2010) Mol Cell Biol 30, 231-44.
- Eifert, C. et al. (2006) Mol Reprod Dev 73, 796-824.
- Mark, M. et al. (2006) Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 46, 451-80.
- Niederreither, K. and Dollé, P. (2008) Nat Rev Genet 9, 541-53.
- Mark, M. et al. (2009) Nucl Recept Signal 7, e002.
- Dollé, P. (2009) Nucl Recept Signal 7, e006.
- Purton, L.E. et al. (2006) J Exp Med 203, 1283-93.
- Fisher, G.J. et al. (1994) J Biol Chem 269, 20629-35.
- Zelent, A. et al. (1989) Nature 339, 714-7.
- Elder, J.T. et al. (1991) J Invest Dermatol 96, 425-33.
- Giannì, M. et al. (2002) EMBO J 21, 3760-9.
- Gronemeyer, H. et al. (2004) Nat Rev Drug Discov 3, 950-64.
- Mangelsdorf, D.J. et al. (1992) Genes Dev 6, 329-44.
Background References
Trademarks and Patents
使用に関する制限
法的な権限を与えられたCSTの担当者が署名した書面によって別途明示的に合意された場合を除き、 CST、その関連会社または代理店が提供する製品には以下の条件が適用されます。お客様が定める条件でここに定められた条件に含まれるものを超えるもの、 または、ここに定められた条件と異なるものは、法的な権限を与えられたCSTの担当者が別途書面にて受諾した場合を除き、拒絶され、 いかなる効力も効果も有しません。
研究専用 (For Research Use Only) またはこれに類似する表示がされた製品は、 いかなる目的についても FDA または外国もしくは国内のその他の規制機関により承認、認可または許可を受けていません。 お客様は製品を診断もしくは治療目的で使用してはならず、また、製品に表示された内容に違反する方法で使用してはなりません。 CST が販売または使用許諾する製品は、エンドユーザーであるお客様に対し、使途を研究および開発のみに限定して提供されるものです。 診断、予防もしくは治療目的で製品を使用することまたは製品を再販売 (単独であるか他の製品等の一部であるかを問いません) もしくはその他の商業的利用の目的で購入することについては、CST から別途許諾を得る必要があります。 お客様は以下の事項を遵守しなければなりません。(a) CST の製品 (単独であるか他の資材と一緒であるかを問いません) を販売、使用許諾、貸与、寄付もしくはその他の態様で第三者に譲渡したり使用させたりしてはなりません。また、商用の製品を製造するために CST の製品を使用してはなりません。(b) 複製、改変、リバースエンジニアリング、逆コンパイル、 分解または他の方法により製品の構造または技術を解明しようとしてはなりません。また、 CST の製品またはサービスと競合する製品またはサービスを開発する目的で CST の製品を使用してはなりません。(c) CST の製品の商標、商号、ロゴ、特許または著作権に関する通知または表示を除去したり改変したりしてはなりません。(d) CST の製品をCST 製品販売条件(CST’s Product Terms of Sale) および該当する書面のみに従って使用しなければなりません。(e) CST の製品に関連してお客様が使用する第三者の製品またはサービスに関する使用許諾条件、 サービス提供条件またはこれに類する合意事項を遵守しなければなりません。