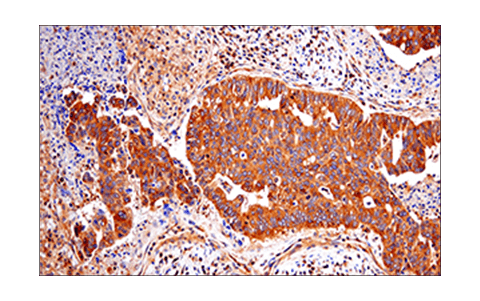
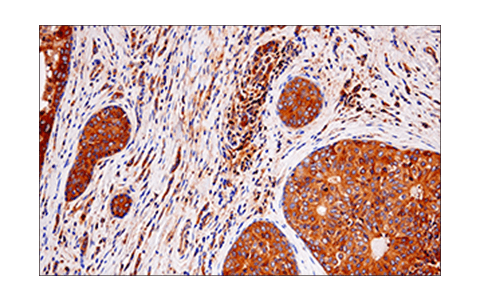
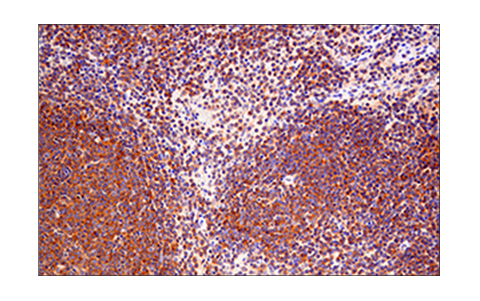
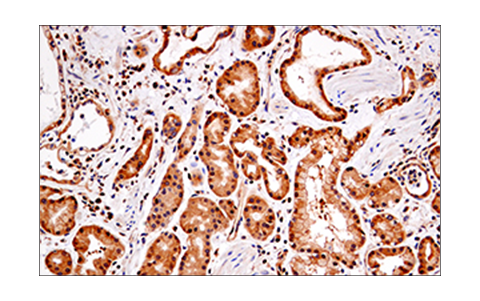
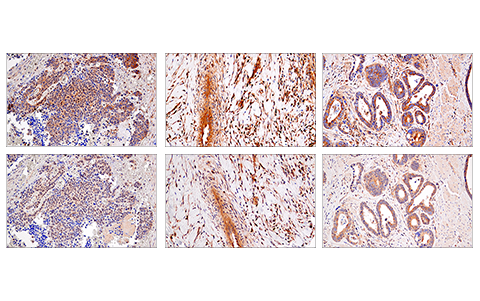
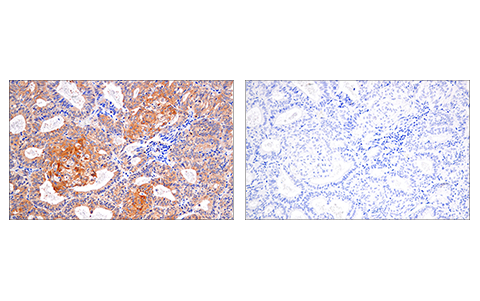
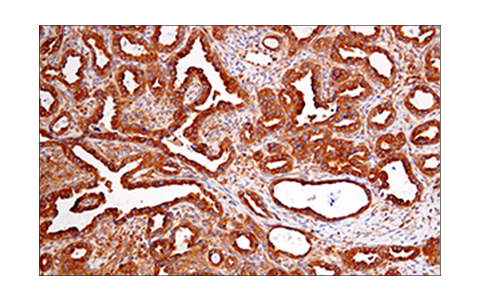
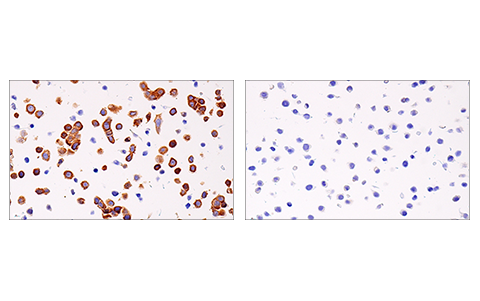
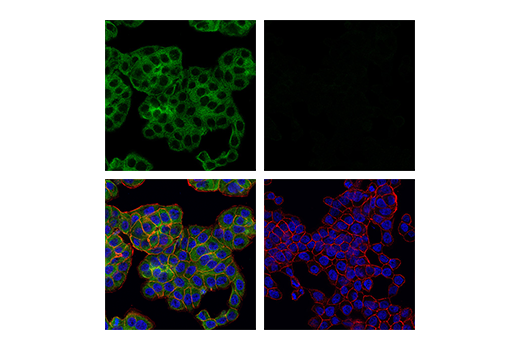
WB, IP, IHC-P, IF-IC
H
Endogenous
78
Rabbit IgG
#Q13546
8737
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunoprecipitation | 1:200 |
| Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) | 1:300 - 1:1200 |
| Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) | 1:800 |
Storage
For a carrier free (BSA and azide free) version of this product see product #81295.
Specificity / Sensitivity
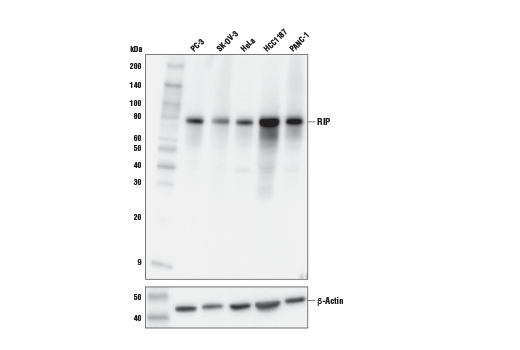
Species Reactivity:
Human
Source / Purification
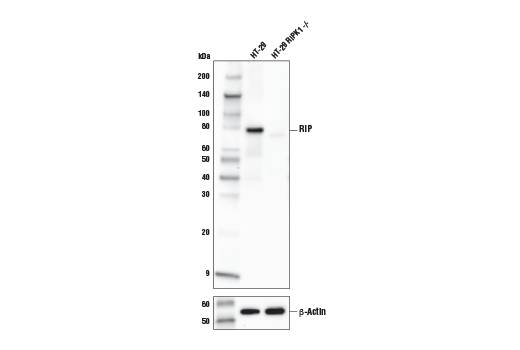
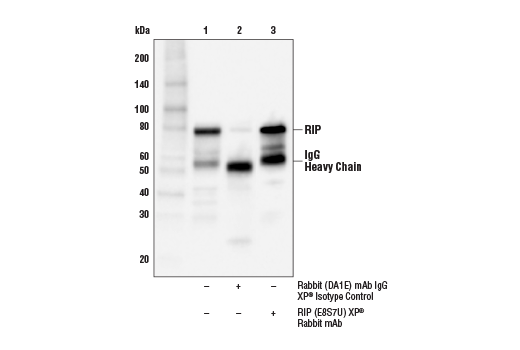
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues surrounding Arg424 of human RIP protein.
Background
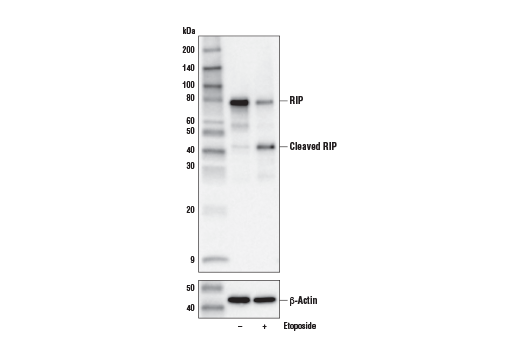
The receptor-interacting protein (RIP) family of serine-threonine kinases (RIP, RIP2, RIP3, and RIP4) are important regulators of cellular stress that trigger pro-survival and inflammatory responses through the activation of NF-κB, as well as pro-apoptotic pathways (1). In addition to the kinase domain, RIP contains a death domain responsible for interaction with the death domain receptor Fas and recruitment to TNF-R1 through interaction with TRADD (2,3). RIP-deficient cells show a failure in TNF-mediated NF-κB activation, making the cells more sensitive to apoptosis (4,5). RIP also interacts with TNF-receptor-associated factors (TRAFs) and can recruit IKKs to the TNF-R1 signaling complex via interaction with NEMO, leading to IκB phosphorylation and degradation (6,7). Overexpression of RIP induces both NF-κB activation and apoptosis (2,3). Caspase-8-dependent cleavage of the RIP death domain can trigger the apoptotic activity of RIP (8).
Necroptosis, a regulated pathway for necrotic cell death, is triggered by a number of inflammatory signals including cytokines in the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family, pathogen sensors such as toll-like receptors (TLRs), and ischemic injury (9,10). The process is negatively regulated by caspases and is initiated through a complex containing the RIP and RIP3 kinases, typically referred to as the necrosome. Necroptosis is inhibited by a small molecule inhibitor of RIP, necrostatin-1 (Nec-1) (11). Research studies show that necroptosis contributes to a number of pathological conditions, and Nec-1 has been shown to provide neuroprotection in models such as ischemic brain injury (12). RIP is phosphorylated at several sites within the kinase domain that are sensitive to Nec-1, including Ser14, Ser15, Ser161, and Ser166 (13).
- Meylan, E. and Tschopp, J. (2005) Trends Biochem Sci 30, 151-9.
- Hsu, H. et al. (1996) Immunity 4, 387-96.
- Stanger, B.Z. et al. (1995) Cell 81, 513-23.
- Ting, A.T. et al. (1996) EMBO J 15, 6189-96.
- Kelliher, M.A. et al. (1998) Immunity 8, 297-303.
- Devin, A. et al. (2000) Immunity 12, 419-29.
- Zhang, S.Q. et al. (2000) Immunity 12, 301-11.
- Lin, Y. et al. (1999) Genes Dev 13, 2514-26.
- Christofferson, D.E. and Yuan, J. (2010) Curr Opin Cell Biol 22, 263-8.
- Kaczmarek, A. et al. (2013) Immunity 38, 209-23.
- Degterev, A. et al. (2008) Nat Chem Biol 4, 313-21.
- Degterev, A. et al. (2005) Nat Chem Biol 1, 112-9.
- Ofengeim, D. and Yuan, J. (2013) Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14, 727-36.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Western Blot Buffer
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 5% w/v BSA, 1X TBS, 0.1% Tween® 20 at 4°C with gentle shaking, overnight.
Applications Key
WB: Western Blotting IP: Immunoprecipitation IHC-P: Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) IF-IC: Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry)
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
使用に関する制限
法的な権限を与えられたCSTの担当者が署名した書面によって別途明示的に合意された場合を除き、 CST、その関連会社または代理店が提供する製品には以下の条件が適用されます。お客様が定める条件でここに定められた条件に含まれるものを超えるもの、 または、ここに定められた条件と異なるものは、法的な権限を与えられたCSTの担当者が別途書面にて受諾した場合を除き、拒絶され、 いかなる効力も効果も有しません。
研究専用 (For Research Use Only) またはこれに類似する表示がされた製品は、 いかなる目的についても FDA または外国もしくは国内のその他の規制機関により承認、認可または許可を受けていません。 お客様は製品を診断もしくは治療目的で使用してはならず、また、製品に表示された内容に違反する方法で使用してはなりません。 CST が販売または使用許諾する製品は、エンドユーザーであるお客様に対し、使途を研究および開発のみに限定して提供されるものです。 診断、予防もしくは治療目的で製品を使用することまたは製品を再販売 (単独であるか他の製品等の一部であるかを問いません) もしくはその他の商業的利用の目的で購入することについては、CST から別途許諾を得る必要があります。 お客様は以下の事項を遵守しなければなりません。(a) CST の製品 (単独であるか他の資材と一緒であるかを問いません) を販売、使用許諾、貸与、寄付もしくはその他の態様で第三者に譲渡したり使用させたりしてはなりません。また、商用の製品を製造するために CST の製品を使用してはなりません。(b) 複製、改変、リバースエンジニアリング、逆コンパイル、 分解または他の方法により製品の構造または技術を解明しようとしてはなりません。また、 CST の製品またはサービスと競合する製品またはサービスを開発する目的で CST の製品を使用してはなりません。(c) CST の製品の商標、商号、ロゴ、特許または著作権に関する通知または表示を除去したり改変したりしてはなりません。(d) CST の製品をCST 製品販売条件(CST’s Product Terms of Sale) および該当する書面のみに従って使用しなければなりません。(e) CST の製品に関連してお客様が使用する第三者の製品またはサービスに関する使用許諾条件、 サービス提供条件またはこれに類する合意事項を遵守しなければなりません。