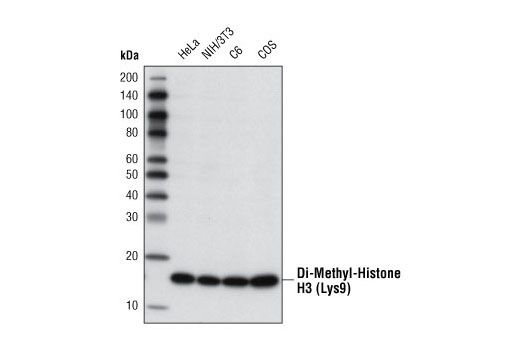
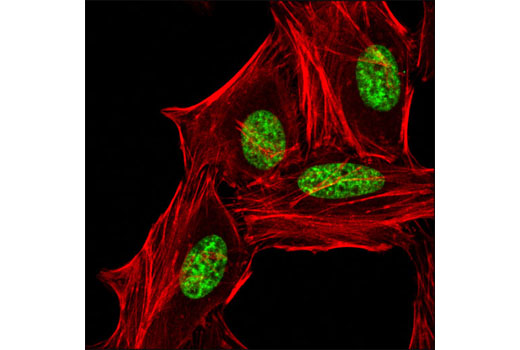
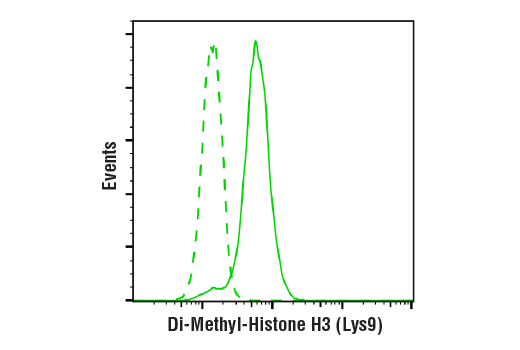
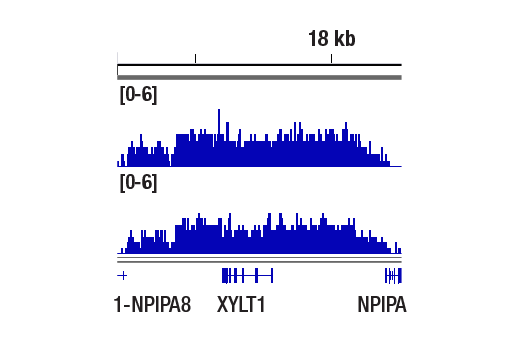
WB, IP, IF-IC, FC-FP, ChIP, ChIP-seq, C&T
H M R Mk
Endogenous
17
Rabbit IgG
#P68431
8350
Product Information
Product Usage Information
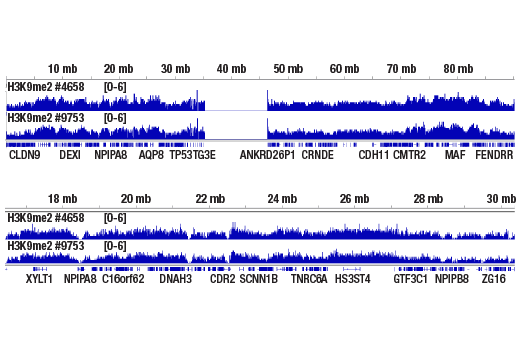
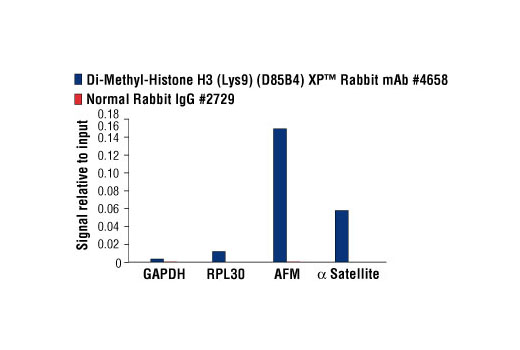
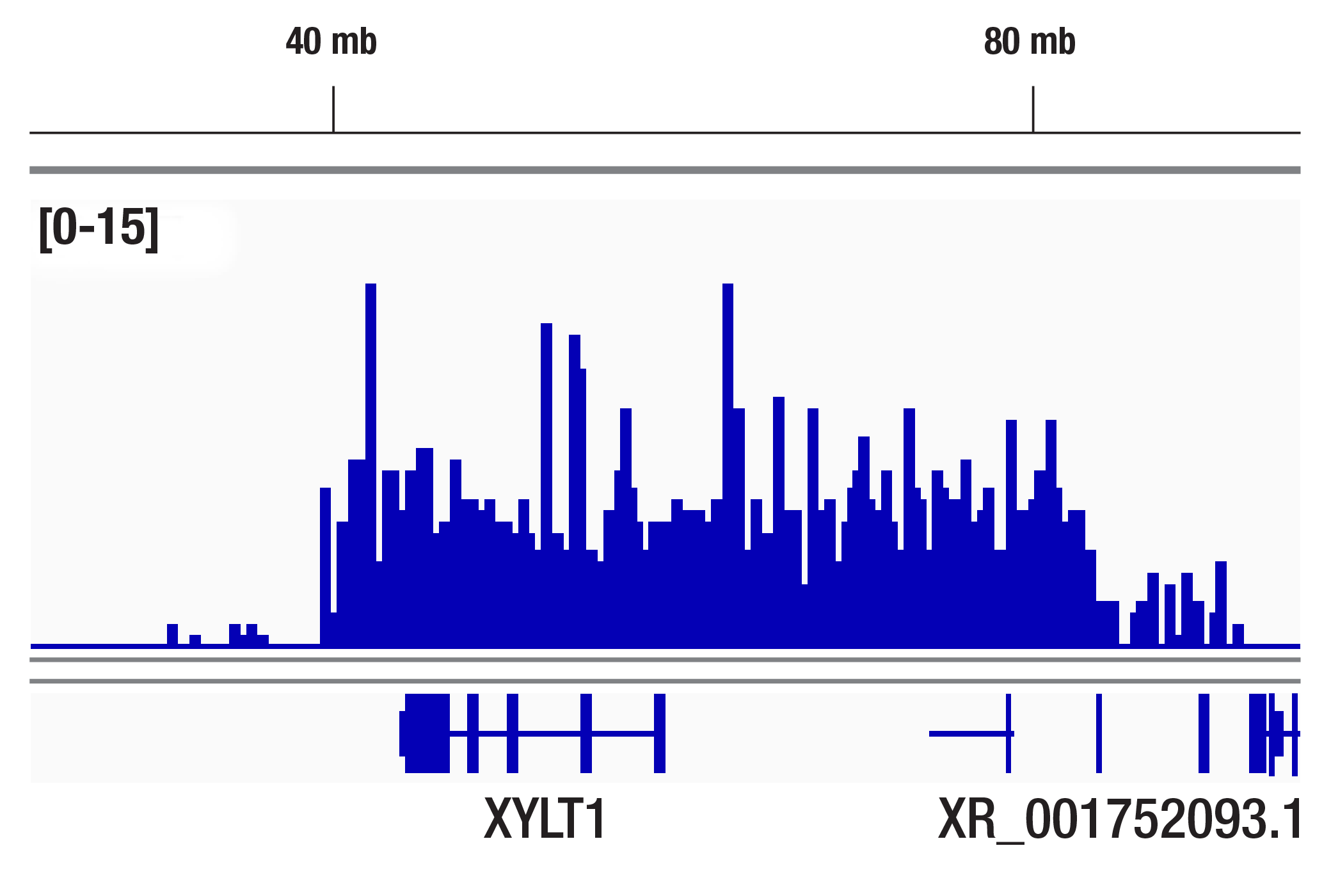
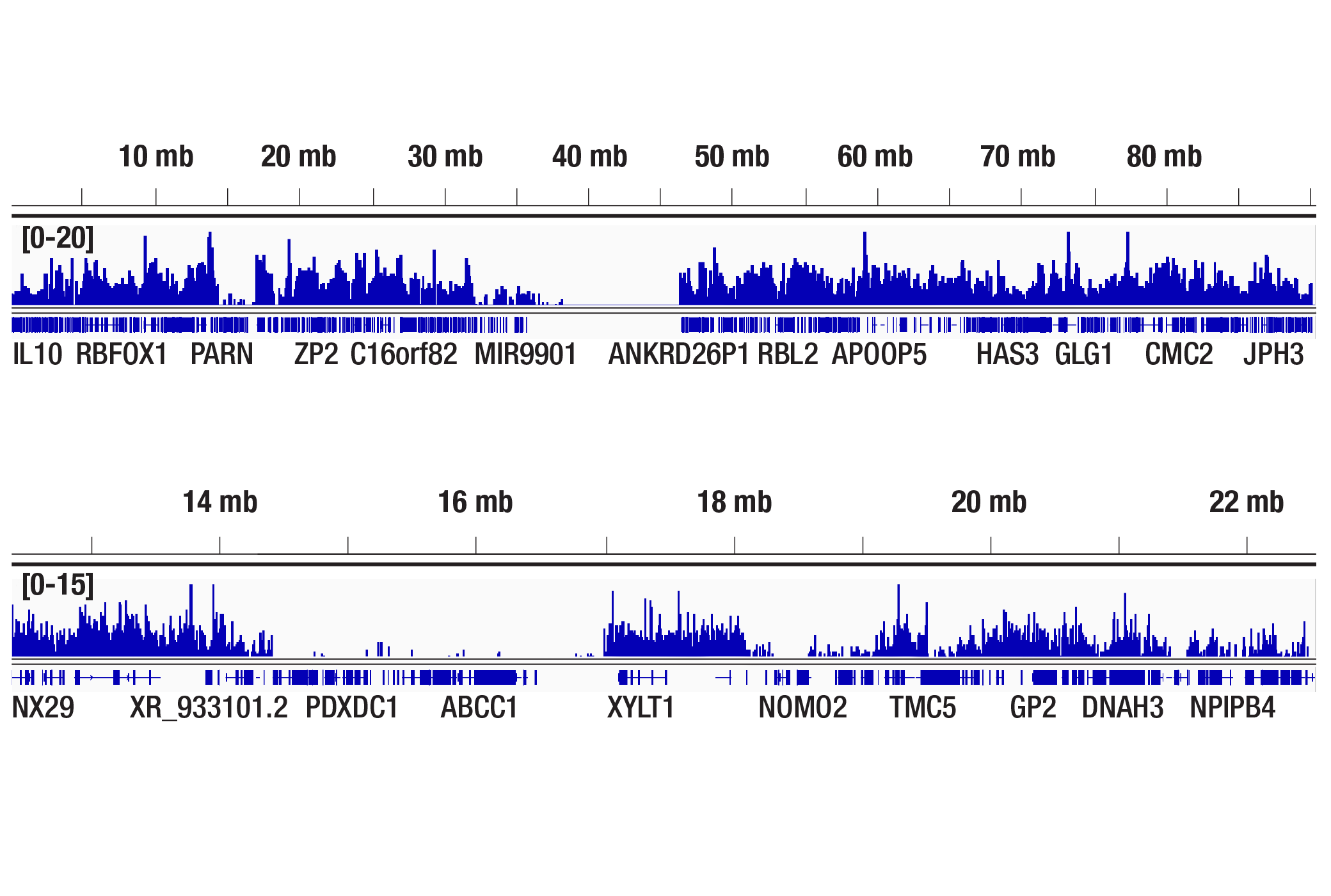
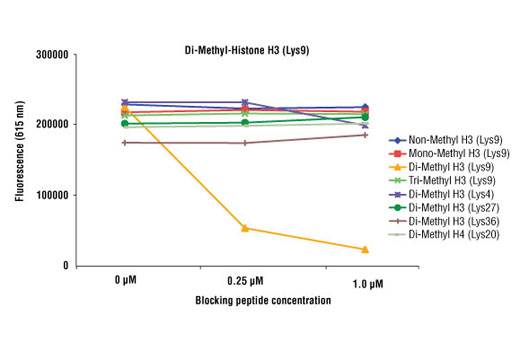
For optimal ChIP and ChIP-seq results, use 10 μl of antibody and 10 μg of chromatin (approximately 4 x 106 cells) per IP. This antibody has been validated using SimpleChIP® Enzymatic Chromatin IP Kits.
The CUT&Tag dilution was determined using CUT&Tag Assay Kit #77552.
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunoprecipitation | 1:50 |
| Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) | 1:200 - 1:800 |
| Flow Cytometry (Fixed/Permeabilized) | 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Chromatin IP | 1:50 |
| Chromatin IP-seq | 1:50 |
| CUT&Tag | 1:50 |
Storage
For a carrier free (BSA and azide free) version of this product see product #80806.
Specificity / Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey
Species predicted to react based on 100% sequence homology
The antigen sequence used to produce this antibody shares
100% sequence homology with the species listed here, but
reactivity has not been tested or confirmed to work by CST.
Use of this product with these species is not covered under
our
Product Performance Guarantee.
D. melanogaster, Xenopus, Zebrafish, Bovine, Pig, S. cerevisiae, C. elegans, Rabbit
Source / Purification
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide corresponding to the amino terminus of histone H3 in which Lys9 is di-methylated.
Background
The nucleosome, made up of four core histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4), is the primary building block of chromatin. Originally thought to function as a static scaffold for DNA packaging, histones have now been shown to be dynamic proteins, undergoing multiple types of post-translational modifications, including acetylation, phosphorylation, methylation, and ubiquitination (1). Histone methylation is a major determinant for the formation of active and inactive regions of the genome and is crucial for the proper programming of the genome during development (2,3). Arginine methylation of histones H3 (Arg2, 17, 26) and H4 (Arg3) promotes transcriptional activation and is mediated by a family of protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs), including the co-activators PRMT1 and CARM1 (PRMT4) (4). In contrast, a more diverse set of histone lysine methyltransferases has been identified, all but one of which contain a conserved catalytic SET domain originally identified in the Drosophila Su(var)3-9, Enhancer of zeste, and Trithorax proteins. Lysine methylation occurs primarily on histones H3 (Lys4, 9, 27, 36, 79) and H4 (Lys20) and has been implicated in both transcriptional activation and silencing (4). Methylation of these lysine residues coordinates the recruitment of chromatin modifying enzymes containing methyl-lysine binding modules such as chromodomains (HP1, PRC1), PHD fingers (BPTF, ING2), tudor domains (53BP1), and WD-40 domains (WDR5) (5-8). The discovery of histone demethylases, such as PADI4, LSD1, JMJD1, JMJD2, and JHDM1, has shown that methylation is a reversible epigenetic marker (9).
- Peterson, C.L. and Laniel, M.A. (2004) Curr Biol 14, R546-51.
- Kubicek, S. et al. (2006) Ernst Schering Res Found Workshop, 1-27.
- Lin, W. and Dent, S.Y. (2006) Curr Opin Genet Dev 16, 137-42.
- Lee, D.Y. et al. (2005) Endocr Rev 26, 147-70.
- Daniel, J.A. et al. (2005) Cell Cycle 4, 919-26.
- Shi, X. et al. (2006) Nature 442, 96-9.
- Wysocka, J. et al. (2006) Nature 442, 86-90.
- Wysocka, J. et al. (2005) Cell 121, 859-72.
- Trojer, P. and Reinberg, D. (2006) Cell 125, 213-7.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Western Blot Buffer
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 5% w/v BSA, 1X TBS, 0.1% Tween® 20 at 4°C with gentle shaking, overnight.
Applications Key
WB: Western Blotting IP: Immunoprecipitation IF-IC: Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) FC-FP: Flow Cytometry (Fixed/Permeabilized) ChIP: Chromatin IP ChIP-seq: Chromatin IP-seq C&T: CUT&Tag
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
使用に関する制限
法的な権限を与えられたCSTの担当者が署名した書面によって別途明示的に合意された場合を除き、 CST、その関連会社または代理店が提供する製品には以下の条件が適用されます。お客様が定める条件でここに定められた条件に含まれるものを超えるもの、 または、ここに定められた条件と異なるものは、法的な権限を与えられたCSTの担当者が別途書面にて受諾した場合を除き、拒絶され、 いかなる効力も効果も有しません。
研究専用 (For Research Use Only) またはこれに類似する表示がされた製品は、 いかなる目的についても FDA または外国もしくは国内のその他の規制機関により承認、認可または許可を受けていません。 お客様は製品を診断もしくは治療目的で使用してはならず、また、製品に表示された内容に違反する方法で使用してはなりません。 CST が販売または使用許諾する製品は、エンドユーザーであるお客様に対し、使途を研究および開発のみに限定して提供されるものです。 診断、予防もしくは治療目的で製品を使用することまたは製品を再販売 (単独であるか他の製品等の一部であるかを問いません) もしくはその他の商業的利用の目的で購入することについては、CST から別途許諾を得る必要があります。 お客様は以下の事項を遵守しなければなりません。(a) CST の製品 (単独であるか他の資材と一緒であるかを問いません) を販売、使用許諾、貸与、寄付もしくはその他の態様で第三者に譲渡したり使用させたりしてはなりません。また、商用の製品を製造するために CST の製品を使用してはなりません。(b) 複製、改変、リバースエンジニアリング、逆コンパイル、 分解または他の方法により製品の構造または技術を解明しようとしてはなりません。また、 CST の製品またはサービスと競合する製品またはサービスを開発する目的で CST の製品を使用してはなりません。(c) CST の製品の商標、商号、ロゴ、特許または著作権に関する通知または表示を除去したり改変したりしてはなりません。(d) CST の製品をCST 製品販売条件(CST’s Product Terms of Sale) および該当する書面のみに従って使用しなければなりません。(e) CST の製品に関連してお客様が使用する第三者の製品またはサービスに関する使用許諾条件、 サービス提供条件またはこれに類する合意事項を遵守しなければなりません。