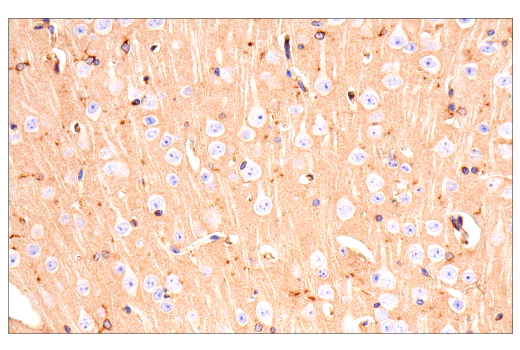
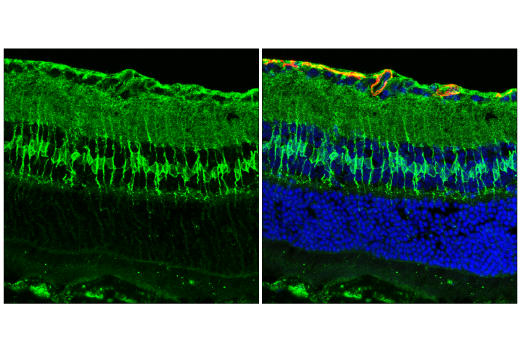
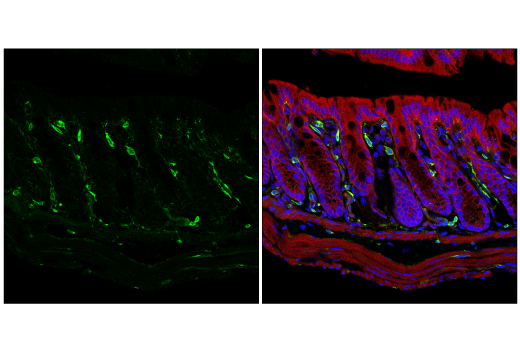
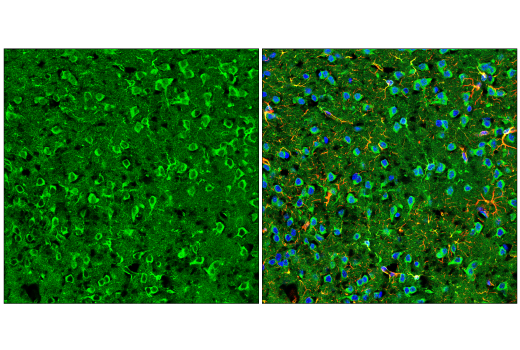
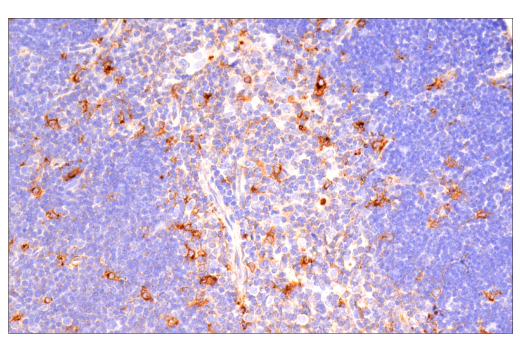
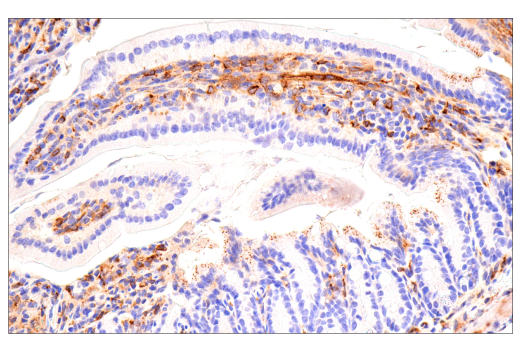
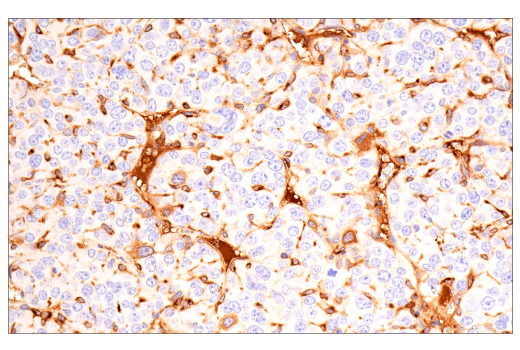
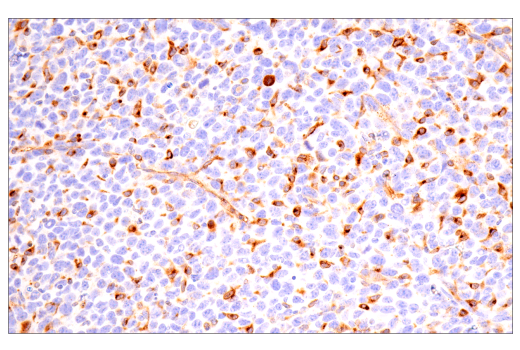
| Product Includes | Product # | Quantity | Mol. Wt | Isotype/Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
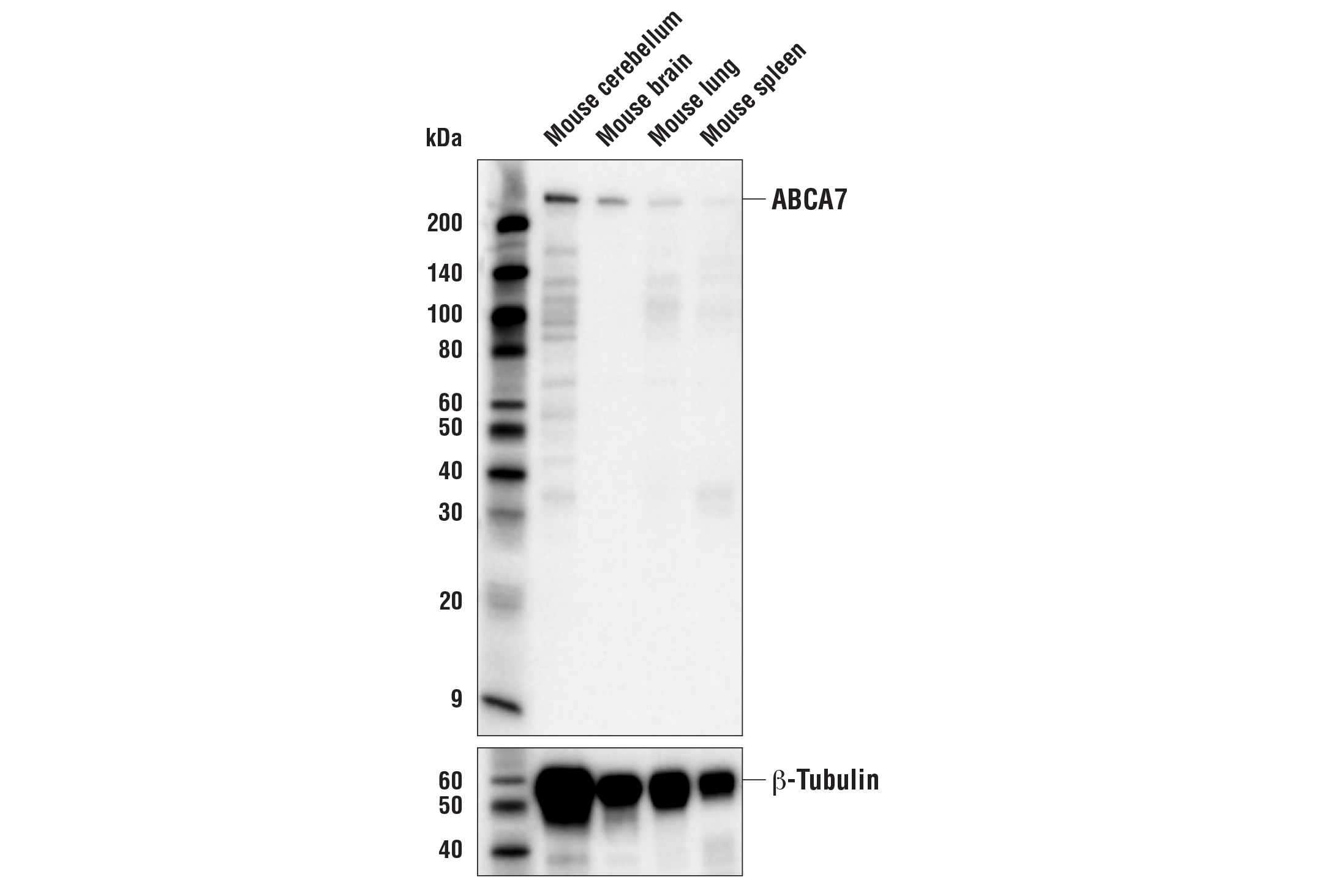
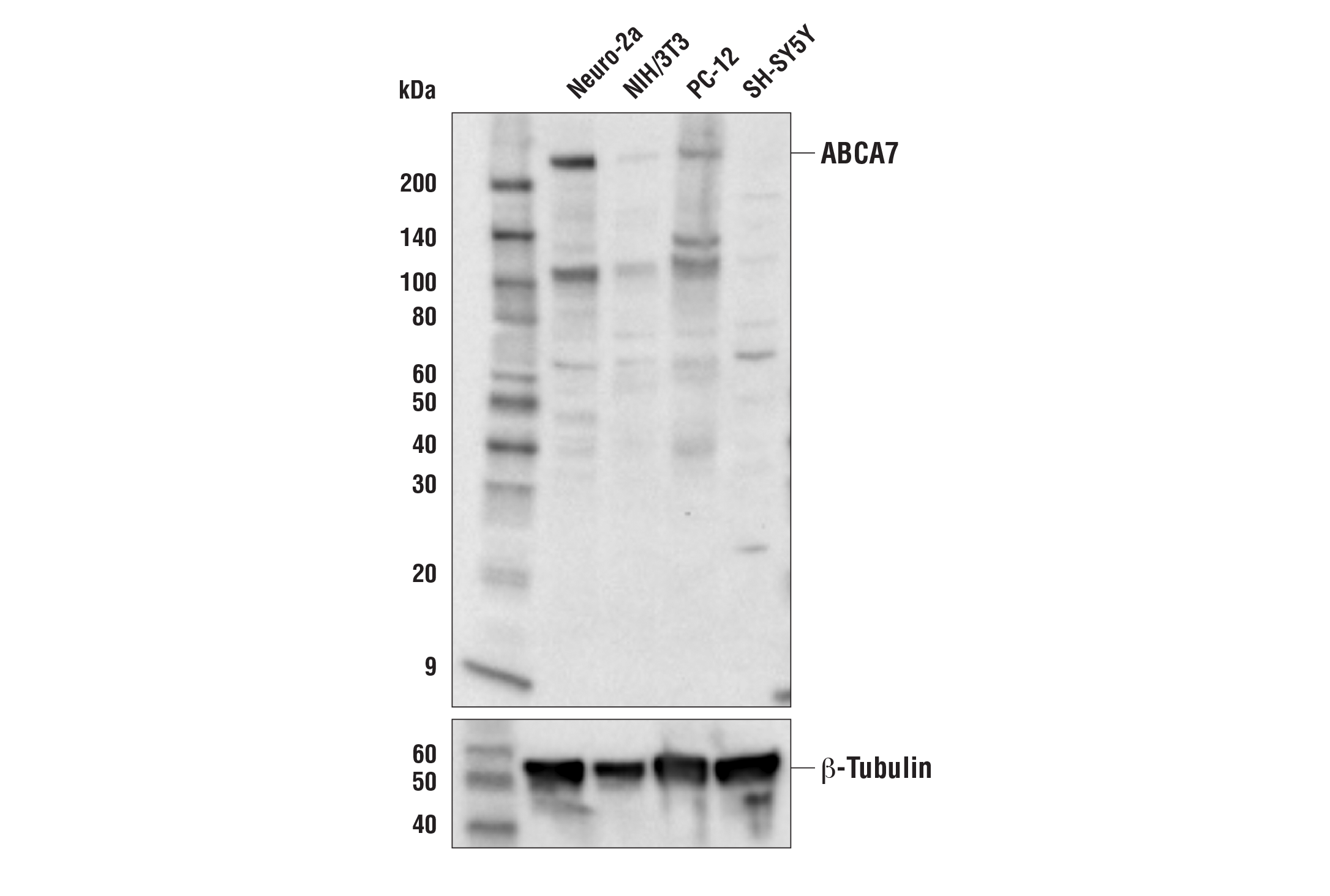
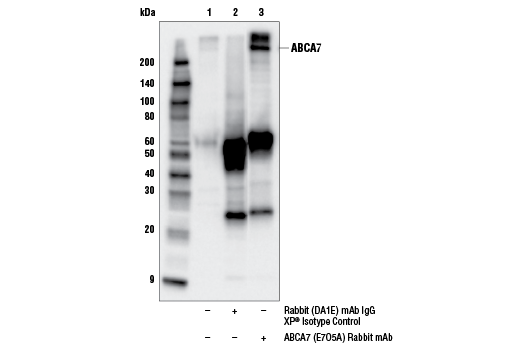
| ABCA7 (E7O5A) Rabbit mAb | 32942 | 20 µl | 235 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
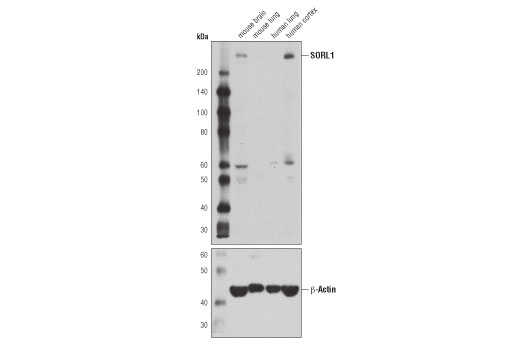
| SORL1 (D8D4G) Rabbit mAb | 79322 | 20 µl | 250 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
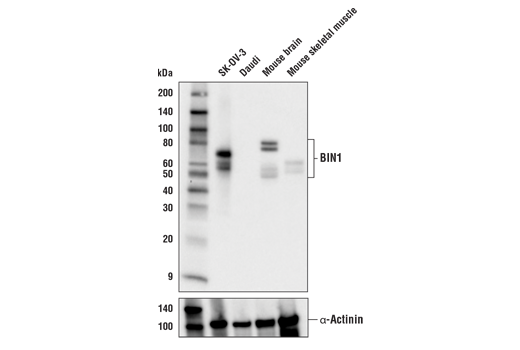
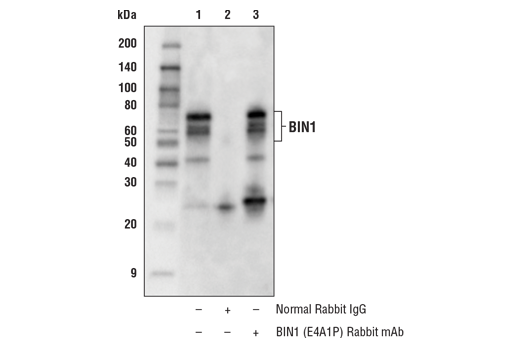
| BIN1 (E4A1P) Rabbit mAb | 51844 | 20 µl | 45-80 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
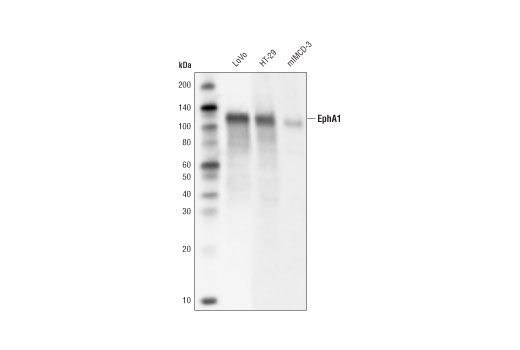
| EphA1 (D6V7I) Rabbit mAb | 90673 | 20 µl | 130 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
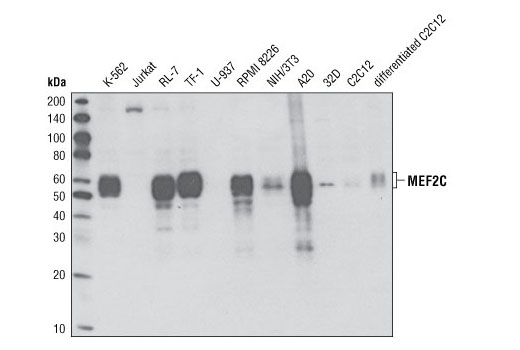
| MEF2C (D80C1) XP® Rabbit mAb | 5030 | 20 µl | 50-60 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
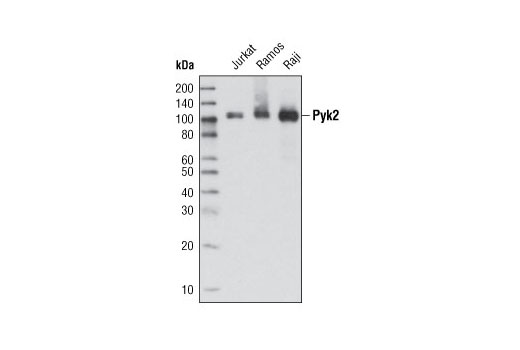
| Pyk2 (5E2) Mouse mAb | 3480 | 20 µl | 116 kDa | Mouse IgG2a |
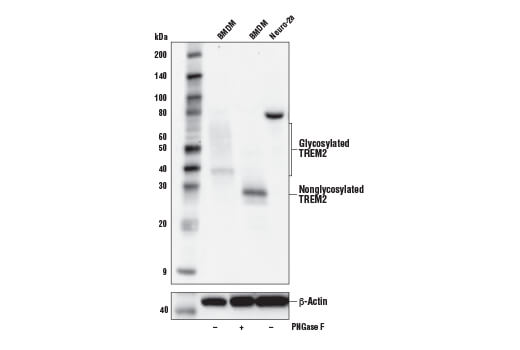
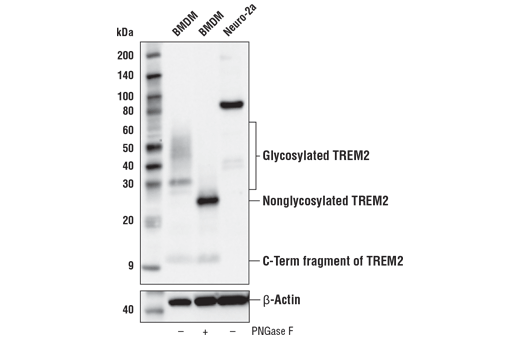
| TREM2 (E6T1P) Rabbit mAb (Amino-terminal Antigen) | 61788 | 20 µl | 28 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
| TREM2 (E7P8J) Rabbit mAb (Carboxy-terminal Antigen) | 76765 | 20 µl | 11, 28 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
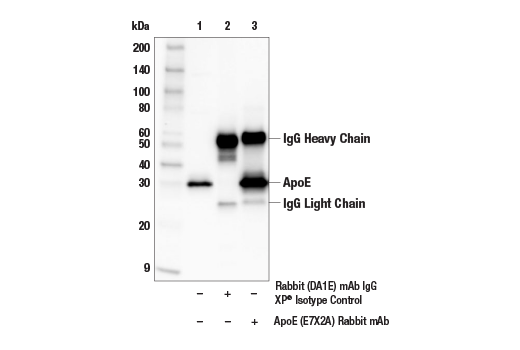
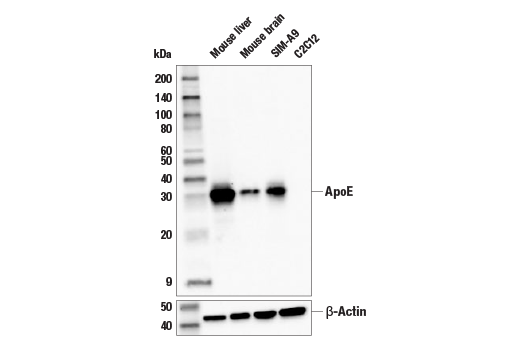
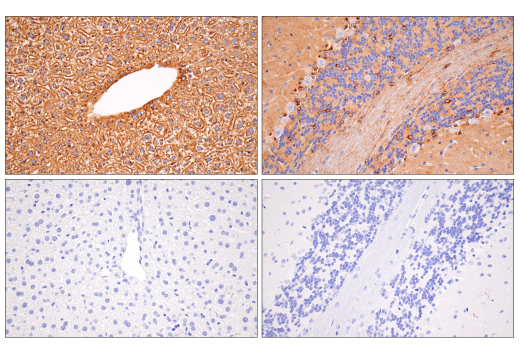
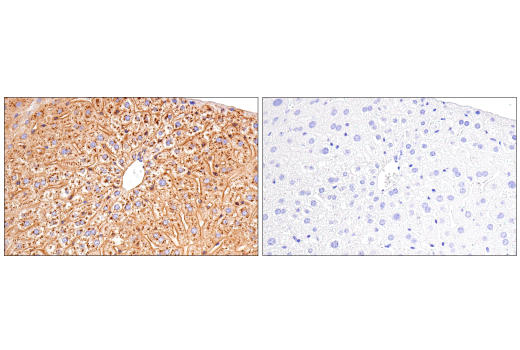
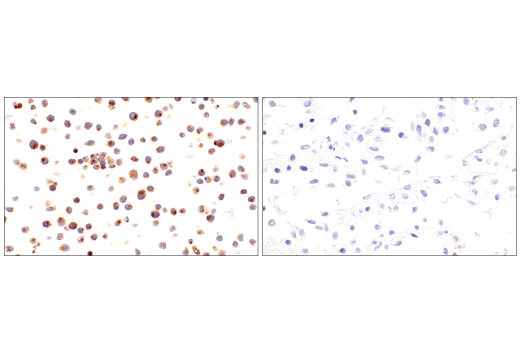
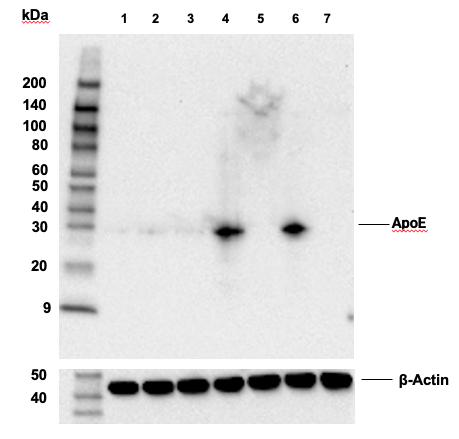
| ApoE (E7X2A) Rabbit mAb | 49285 | 20 µl | 35 kDa | Rabbit IgG |
| Anti-rabbit IgG, HRP-linked Antibody | 7074 | 100 µl | Goat |
Please visit cellsignal.com for individual component applications, species cross-reactivity, dilutions, protocols, and additional product information.
Description
The Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease Risk Gene (Mouse Model) Antibody Sampler Kit provides an economical means of detecting proteins identified as risk factors for late-onset Alzheimer’s Disease (LOAD) by western blot. This kit includes enough antibodies to perform at least two western blot experiments with each primary antibody.
Storage
Background
Alzheimer's Disease (AD) is the leading cause of dementia worldwide. Clinically, it is characterized by the presence of extracellular amyloid plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles, which result in neuronal dysfunction and cell death (1). Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified a cohort of risk genes associated with late-onset AD (LOAD), including, but not limited to, APOE, BIN1, SORL1, TREM2, EphA1, MEF2C, ABCA7, and PTK2B (2).
APOE has three allele variants; ApoE2, ApoE3, and ApoE4; with ApoE4 associated with an increased risk of AD. Evidence suggests that this risk occurs through promotion of amyloid-beta plaque aggregation (1). ApoE4 is also associated with impaired microglial response, lipid transport, synaptic integrity and plasticity, glucose metabolism, and cerebrovascular integrity (3). Mutations in BIN1, primarily involved in endocytosis and maintaining cytoskeletal integrity in the brain, are suggested to play a role in the aggravation of tau pathology (4,5). Increased levels of BIN1 have been seen in AD postmortem brain tissue (5). SORL1 expression is decreased in the brain of AD patients (6). Studies have demonstrated a role for SORL1 as a neuronal sorting receptor that binds amyloid precursor protein (APP) and regulates its trafficking and proteolytic processing, thus regulating β-amyloid (Aβ) peptide production (7). The triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) is an innate immune receptor that is expressed on the cell surface of microglia, macrophages, osteoclasts, and immature dendritic cells (8). Research studies using AD mouse models indicate that deficiency and haploinsufficiency of TREM2 can lead to increased Aβ accumulation due to dysfunctional microglia response (9). EphA1 is a member of the ephrin family of receptor tyrosine kinases responsible for regulating cell morphology and motility (10). In the central nervous system (CNS), EphA1 plays a role in synaptic plasticity and axon guidance (11). EphA1 is involved in inflammatory signaling pathways (12), which may mean it plays a role in regulation of neuroinflammatory processes in AD (13). ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 7 (ABCA7) functions to regulate phospholipid and cholesterol homeostasis in the CNS (14,15). ABCA7 dysfunction may contribute directly to AD pathogenesis by accelerating Aβ production and/or altering microglia-dependent phagocytosis of Aβ (16-18). MEF2C is a member of the myocyte enhancer factor 2 (MEF2) family of transcription factors shown to play a role in learning and memory formation through regulation of synaptic plasticity (19). Studies have shown that MEF2C may play a role in age-related microglial activation through IFN-I associated MEF2C deregulation (20,21). MEF2C may also act as a modulator for APP proteolytic processing of Aβ (22,23). Protein tyrosine kinase, Pyk2, encoded by the PTK2B gene, is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase highly expressed in neurons with implications in synaptic plasticity (24,25). In mouse models, knockout of Pyk2 impairs hippocampal-dependent memory and long-term potentiation (24). Overexpression of Pyk2 has been shown to protect neurons against Aβ42-induced synaptotoxicity (26). Pyk2 may also act as a kinase for tau phosphorylation and has been implicated as a modulator of tau toxicity (27,28).
- Selkoe, D.J. (2001) Physiol Rev 81, 741-66.
- Zhang, Q. et al. (2020) Nat Commun 11, 4799.
- Yamazaki, Y. et al. (2019) Nat Rev Neurol 15, 501-518.
- Franzmeier, N. et al. (2019) Nat Commun 10, 1766.
- Chapuis, J. et al. (2013) Mol Psychiatry 18, 1225-34.
- Scherzer, C.R. et al. (2004) Arch Neurol 61, 1200-5.
- Andersen, O.M. et al. (2005) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102, 13461-6.
- Colonna, M. (2003) Nat Rev Immunol 3, 445-53.
- Wang, Y. et al. (2015) Cell 160, 1061-71.
- Yamazaki, T. et al. (2009) J Cell Sci 122, 243-55.
- Lai, K.O. and Ip, N.Y. (2009) Curr Opin Neurobiol 19, 275-83.
- Ivanov, A.I. and Romanovsky, A.A. (2006) IUBMB Life 58, 389-94.
- Villegas-Llerena, C. et al. (2016) Curr Opin Neurobiol 36, 74-81.
- Abe-Dohmae, S. et al. (2004) J Biol Chem 279, 604-11.
- Wang, N. et al. (2003) J Biol Chem 278, 42906-12.
- Pereira, C.D. et al. (2018) J Alzheimers Dis 61, 463-485.
- Fu, Y. et al. (2016) J Alzheimers Dis 54, 569-84.
- Aikawa, T. et al. (2018) Brain Sci 8, 27.
- Rashid, A.J. et al. (2014) Genes Brain Behav 13, 118-25.
- Xue, F. et al. (2021) Neurobiol Dis 152, 105272.
- Deczkowska, A. et al. (2017) Nat Commun 8, 717.
- Tang, S.S. et al. (2016) Oncotarget 7, 39136-39142.
- Camargo, L.M. et al. (2015) PLoS One 10, e0115369.
- Giralt, A. et al. (2017) Nat Commun 8, 15592.
- Mastrolia, V. et al. (2021) Sci Rep 11, 16357.
- Kilinc, D. et al. (2020) Brain Commun 2, fcaa139.
- Li, C. and Götz, J. (2018) J Alzheimers Dis 64, 205-221.
- Dourlen, P. et al. (2017) Mol Psychiatry 22, 874-883.
Background References
Trademarks and Patents
使用に関する制限
法的な権限を与えられたCSTの担当者が署名した書面によって別途明示的に合意された場合を除き、 CST、その関連会社または代理店が提供する製品には以下の条件が適用されます。お客様が定める条件でここに定められた条件に含まれるものを超えるもの、 または、ここに定められた条件と異なるものは、法的な権限を与えられたCSTの担当者が別途書面にて受諾した場合を除き、拒絶され、 いかなる効力も効果も有しません。
研究専用 (For Research Use Only) またはこれに類似する表示がされた製品は、 いかなる目的についても FDA または外国もしくは国内のその他の規制機関により承認、認可または許可を受けていません。 お客様は製品を診断もしくは治療目的で使用してはならず、また、製品に表示された内容に違反する方法で使用してはなりません。 CST が販売または使用許諾する製品は、エンドユーザーであるお客様に対し、使途を研究および開発のみに限定して提供されるものです。 診断、予防もしくは治療目的で製品を使用することまたは製品を再販売 (単独であるか他の製品等の一部であるかを問いません) もしくはその他の商業的利用の目的で購入することについては、CST から別途許諾を得る必要があります。 お客様は以下の事項を遵守しなければなりません。(a) CST の製品 (単独であるか他の資材と一緒であるかを問いません) を販売、使用許諾、貸与、寄付もしくはその他の態様で第三者に譲渡したり使用させたりしてはなりません。また、商用の製品を製造するために CST の製品を使用してはなりません。(b) 複製、改変、リバースエンジニアリング、逆コンパイル、 分解または他の方法により製品の構造または技術を解明しようとしてはなりません。また、 CST の製品またはサービスと競合する製品またはサービスを開発する目的で CST の製品を使用してはなりません。(c) CST の製品の商標、商号、ロゴ、特許または著作権に関する通知または表示を除去したり改変したりしてはなりません。(d) CST の製品をCST 製品販売条件(CST’s Product Terms of Sale) および該当する書面のみに従って使用しなければなりません。(e) CST の製品に関連してお客様が使用する第三者の製品またはサービスに関する使用許諾条件、 サービス提供条件またはこれに類する合意事項を遵守しなければなりません。