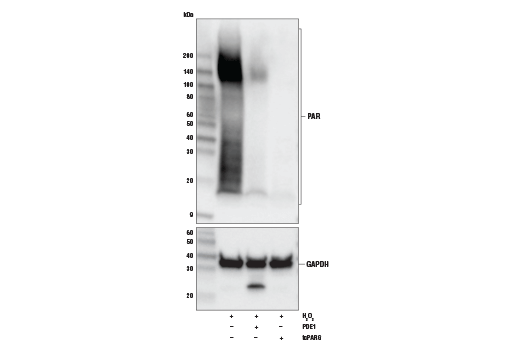
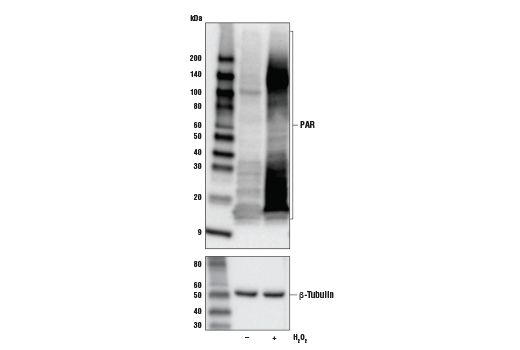
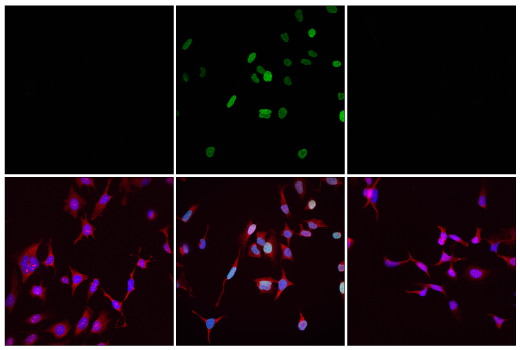
WB, IF-IC
All
Endogenous
Rabbit IgG
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) | 1:12000 - 1:48000 |
Storage
Specificity / Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
All Species Expected
Source / Purification
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with KLH modified on lysines with ADP ribose.
Background
ADP-ribosylation is a post-translational modification that has been described to occur on the side chain of several acceptor residues (lysine, arginine, glutamate, aspartate, cysteine, serine) and protein amino termini as well as on DNA and tRNA (1). ADP-ribosyl transferases (ADPRTs) catalyze the transfer of ADP-ribose from β-NAD+ and release nicotinamide in the process. Mono-ADP-ribosyl transferases (MARTs, or monoPARPs) comprise the vast majority of the ADPRTs. These monoenzymes, which include the sirtuins and many of the PARP (ARTD) and ART proteins, transfer a single ADP-ribose unit to the target residue (MARylation). The poly-ADP-ribose polymerases (polyPARPs) or polyenzymes, which include human PARP1, 2, 5a and 5b, are the most widely studied and can polymerize linear or branched chains of up to ~200 ADPR units (2). Specificity is determined primarily, but not exclusively, by a nonconsecutive catalytic triad motif, with some exceptions. Those containing the R-S-E motif like Cholera toxin are arginine-directed transferases, while those containing the H-Y-E triad tend to exhibit polymerase activity (3,4). ADP-ribosylation is reversible and can be degraded down to a single ADP-ribose unit by poly-ADP-ribose glycohydrolase (PARG) or ADP-ribosylhydrolase 3 (ARH3) or completely removed from the target residue by ARH1, TARG1, MacroD1 or MacroD2 (5).
ADP-ribosylation is involved in a variety of cellular processes, including mitotic spindle formation, chromatin decondensation, cell stress response, retroviral silencing, RNA biology, and transcription, but the most well-known function of ADP-ribose chains is to serve as a scaffold for recruiting DNA repair proteins that contain PAR-binding modules to sites of DNA damage (6). X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 1 (XRCC1), histone macroH2A1, RNF146 (Iduna) an E3 ubiquitin ligase, and many of the PARPs themselves, among others, contain PAR-binding motifs (PBMs) or domains: WWE, PAR-binding zinc-finger (PBZ), or macrodomains (7). PARylation has a central role in cell survival, and is tightly regulated. PARP deficiency can leave a cell vulnerable to DNA damage-induced apoptosis, while hyper PARylation can lead to parthanatos, a unique form of cell death (8). The role of PARylation in DNA repair has inspired great interest in developing candidate drug inhibitors for PARP, in particular to treat breast, prostate and small cell lung cancers with mutations in DNA repair genes like BRCA1/2, CHK2 or ATM. Stat1, PERK, p53, G-actin and Ras are just a few examples of proteins that are functionally modulated by ADP-ribosylation (6,7). Modification by ADP-ribose can block protein interactions or, in the case of P2X7, cause a conformational change that in the presence of ART2 expression sensitizes naive murine T-cells to extracellular NAD+ leading to apoptosis (9).
- Koch-Nolte, F. et al. (2008) Front Biosci 13, 6716-29.
- Leung, A.K. (2014) J Cell Biol 205, 613-9.
- Laing, S. et al. (2011) Amino Acids 41, 257-69.
- Vyas, S. et al. (2014) Nat Commun 5, 4426.
- Vivelo, C.A. and Leung, A.K. (2015) Proteomics 15, 203-17.
- Gupte, R. et al. (2017) Genes Dev 31, 101-126.
- Wei, H. and Yu, X. (2016) Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 14, 131-139.
- David, K.K. et al. (2009) Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 14, 1116-28.
- Seman, M. et al. (2003) Immunity 19, 571-82.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Western Blot Buffer
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 5% w/v BSA, 1X TBS, 0.1% Tween® 20 at 4°C with gentle shaking, overnight.
Applications Key
WB: Western Blotting IF-IC: Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry)
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
使用に関する制限
法的な権限を与えられたCSTの担当者が署名した書面によって別途明示的に合意された場合を除き、 CST、その関連会社または代理店が提供する製品には以下の条件が適用されます。お客様が定める条件でここに定められた条件に含まれるものを超えるもの、 または、ここに定められた条件と異なるものは、法的な権限を与えられたCSTの担当者が別途書面にて受諾した場合を除き、拒絶され、 いかなる効力も効果も有しません。
研究専用 (For Research Use Only) またはこれに類似する表示がされた製品は、 いかなる目的についても FDA または外国もしくは国内のその他の規制機関により承認、認可または許可を受けていません。 お客様は製品を診断もしくは治療目的で使用してはならず、また、製品に表示された内容に違反する方法で使用してはなりません。 CST が販売または使用許諾する製品は、エンドユーザーであるお客様に対し、使途を研究および開発のみに限定して提供されるものです。 診断、予防もしくは治療目的で製品を使用することまたは製品を再販売 (単独であるか他の製品等の一部であるかを問いません) もしくはその他の商業的利用の目的で購入することについては、CST から別途許諾を得る必要があります。 お客様は以下の事項を遵守しなければなりません。(a) CST の製品 (単独であるか他の資材と一緒であるかを問いません) を販売、使用許諾、貸与、寄付もしくはその他の態様で第三者に譲渡したり使用させたりしてはなりません。また、商用の製品を製造するために CST の製品を使用してはなりません。(b) 複製、改変、リバースエンジニアリング、逆コンパイル、 分解または他の方法により製品の構造または技術を解明しようとしてはなりません。また、 CST の製品またはサービスと競合する製品またはサービスを開発する目的で CST の製品を使用してはなりません。(c) CST の製品の商標、商号、ロゴ、特許または著作権に関する通知または表示を除去したり改変したりしてはなりません。(d) CST の製品をCST 製品販売条件(CST’s Product Terms of Sale) および該当する書面のみに従って使用しなければなりません。(e) CST の製品に関連してお客様が使用する第三者の製品またはサービスに関する使用許諾条件、 サービス提供条件またはこれに類する合意事項を遵守しなければなりません。